
How will a recession affect the healthcare industry?
Recently, there has been substantial talk of an approaching economic recession in the United States. Economic downturns are disruptive to people’s livelihood, with nearly everyone in the economy financially, economically and physically impacted. Yet, the consequences of a recession are not initially visible in the healthcare industry.
What happens to surgical centers during a recession?
Research from 2013 indicated that during severe recessions, people will delay elective-surgical procedures. In turn, these actions create substantial financial headwinds for surgical centers, hospitals and health systems.
What happened to family physicians during the Great Recession?
Previously mentioned research by the American Academy of Family Physicians listed the following trends during the Great Recession: Increase in patients with major stress symptoms. Concerns over the ability to pay for their healthcare needs. Increase in appointment cancellations by patients.
How does the economy affect health care costs?
In the United States, the economy shapes the complex interactions between overall employment, health coverage, medical costs and access to quality care. A variety of details, both seen and unseen, can change the outcome and cost of healthcare.
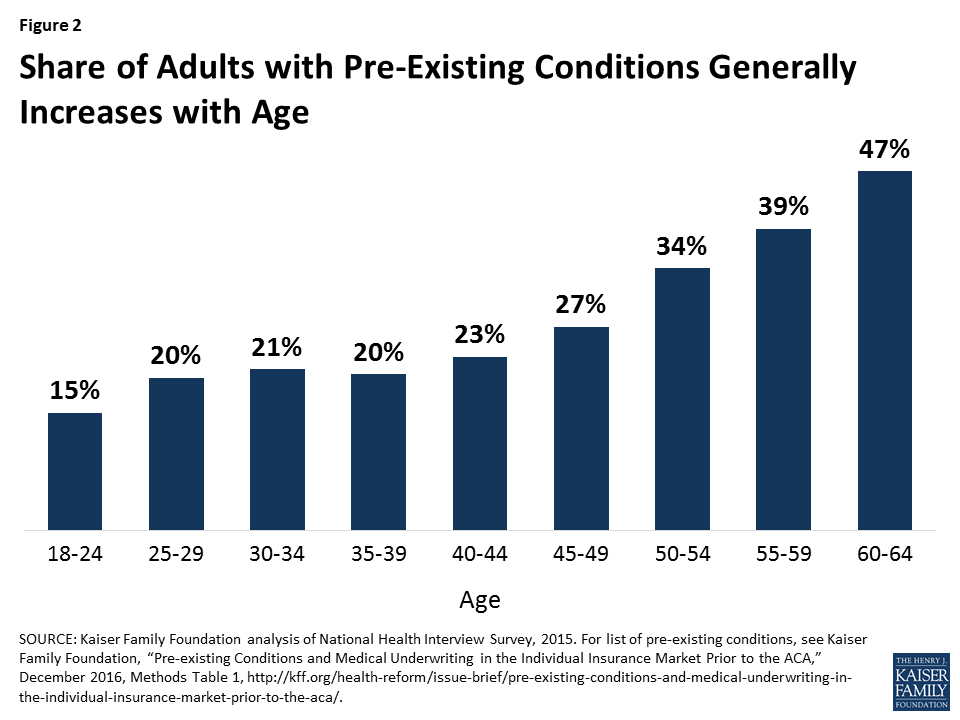
How did the Great Recession affect Medicare?
Few studies have examined the effects of recessions on health-care spending. One study found that during 2007–2009, overall growth in health-care spending fell, but Medicare spending growth increased and greater state unemployment rates were associated with increased Medicare spending per beneficiary.
How does healthcare do in a recession?
According to this article published by The Hill, healthcare spending grew at a much smaller rate in 2008, the year that the last recession began, than it did in 2007. The article states: “Household spending on healthcare grew by 4.3 percent in 2008 compared to 5.9 percent in 2007….
Who benefits during a recession?
Rental agents, landlords, and property management companies can thrive during a recession when renting is likely to become a more appealing option, if not the only one available.
What industries are immune to recession?
5 Recession Resistant Industries.Consumer Staples.Grocery Stores/Discount Retail.Alcoholic Beverages.Cosmetics.Death and Funeral Services.The Bottom Line.
Is healthcare affected by recession?
"Recession leads to unemployment, which can increase exposure to uninsured care and always has," Mr. Jordahl says. "But I think the emergence of the consumer mentality — now more exposed to healthcare costs through the introduction of high-deductible plans — has really changed the dynamic."
Are healthcare jobs recession proof?
Our results indicate that the healthcare sector is stable across past business cycles. If anything, when areas experience more severe local economic downturns, healthcare employment increases. Much remains unknown about how the healthcare sector will fare during the current recession.
How does a recession affect seniors?
Ultimately, the impact of the recession on the wealth of older adults was modest. By 2012, older adults overall had recovered most of the wealth lost during the Great Recession. From 2017 to 2018, the real median income (after adjusting for inflation) of all households headed by older people increased by 3.3%.
What industry does best in a recession?
Healthcare, food, consumer staples, and basic transportation are examples of relatively inelastic industries that can perform well in recessions. They may also benefit from being considered essential industries during a public health emergency like the COVID-19 pandemic.
Who is affected most by a recession?
Although young adults in their 20s and 30s bore the brunt of the economic downturn, many Americans ages 50 and older—including baby boomers nearing retirement—were also affected, either directly or indirectly, by rising unemployment, falling home values, and the decline in the stock market.
Which types of industries are hit hardest by a recession explain?
Retail. The retail industry is one of the nation's largest sectors for employment, with an estimated 15.6 million employees. With that kind of employment, retail workers make up over 11% of the U.S. workforce. In many recessions, the retail trade is hit hardest once those individuals shoppers begin losing jobs.
What thrived during the Great Depression?
Like candy, cigarette sales skyrocketed during the Great Depression, and tobacco stocks are still a smart buy in any recession [source: Gibbons].
Who made money during the Great Depression?
Not everyone, however, lost money during the worst economic downturn in American history. Business titans such as William Boeing and Walter Chrysler actually grew their fortunes during the Great Depression.
Abstract
Previous work has found a strong connection between the most recent economic recession and reductions in private health spending. However, the effect of economic downturns on Medicare spending is less clear.
The Macroeconomy And Medicare Spending
There are several reasons why a prolonged economic downturn might affect health spending by the privately insured. Employers might reduce the generosity of their insurance benefits—witness the sharp increase in high-deductible health plans during the most recent economic slump.
Study Data And Methods
Our data on health spending came from CMS’s county-level aged fee-for-service Medicare spending files, which the federal government uses to determine payment rates for Medicare Advantage plans.
Study Results
In our previous research, we found that privately insured individuals residing in areas that were hardest hit by the recession experienced the greatest reduction in health spending growth.
Why Medicare Spending Is Less Responsive To The Macroeconomy
Above we outlined three ways in which Medicare enrollees could have been affected by the economic downturn: the shock to employment for Medicare enrollees who were still working, the shock to employment of local family members, and declines in enrollees’ housing wealth.
Conclusion
These estimates have both important similarities and differences with the existing estimates in the literature. First, these results provide further support for the argument that the recession was not the primary driver of the slowdown in Medicare spending.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank Clifton Maze and Stephen Heffler at the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) for answering questions about CMS’s Medicare spending data. Johnny Chan provided excellent research assistance. Any remaining errors are those of the authors.
What happens to healthcare during a recession?
When a recession occurs in the United States, the healthcare industry can experience reduced demand for non-urgent or elective care which decreases overall revenue.
How does recession affect patients?
Most industry observers agree that the financial impact of a recession prevents some patients from seeking inpatient treatments and elective services. Offices and institutions may both experience an increase in the number of patients who are unable to pay for the services they have received.
What are the concerns over the ability to pay for their healthcare needs?
Concerns over the ability to pay for their healthcare needs. Increase in appointment cancellations by patients. A decrease in the number of employer-sponsored and privately-insured patients. New health problems developing due to the fact that patients were skipping preventive healthcare measures.
Why do people defer healthcare?
During economic periods when financial margins are constrained, some consumers will defer healthcare in order to save money. A survey by the AAFP (American Academy of Family Physicians) found that some families are forced to prioritize spending on other necessities and reduce spending on health care services.
How much money did hospitals lose in 2011?
From 2009 to 2011, the average 300-bed hospital lost about $3.7 million dollars due to a decline in commercially-insured patients who were unemployment or underemployment. In fact, this change in spending patterns by healthcare consumers helped to permanently change the overall industry.
Is outpatient medicine more affordable?
Most outpatient settings are usually more consumer-friendly and affordable . Particularly, when compared to more traditional inpatient settings. Previously mentioned research by the American Academy of Family Physicians listed the following trends during the Great Recession:
Is healthcare affected by economic downturns?
Many healthcare providers are not always clear as to how an economic slowdown would impact them directly .

The Macroeconomy and Medicare Spending
Study Data and Methods
- Data
Our data on health spending came from CMS’s county-level aged fee-for-service Medicare spending files, which the federal government uses to determine payment rates for Medicare Advantage plans. 21These data track the spending of enrollees in traditional fee-for-service Med… - Methods
We measured the regional severity of the recession using county employment data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics’ Local Area Unemployment Statistics program. We then used Census Bureau estimates to calculate the percentage of the population younger than age sixty-five work…
Study Results
- In our previous research, we found that privately insured individuals residing in areas that were hardest hit by the recession experienced the greatest reduction in health spending growth. 1In our current research, we found a similar pattern for Medicare enrollees, with less labor-force participation associated with larger reductions in health spen...
Why Medicare Spending Is Less Responsive to The Macroeconomy
- Above we outlined three ways in which Medicare enrollees could have been affected by the economic downturn: the shock to employment for Medicare enrollees who were still working, the shock to employment of local family members, and declines in enrollees’ housing wealth. We lacked the data necessary to directly measure the housing wealth of enrollees at sufficiently fin…
Conclusion
- These estimates have both important similarities and differences with the existing estimates in the literature. First, these results provide further support for the argument that the recession was not the primary driver of the slowdown in Medicare spending. 31 For example, Chapin White and coauthors identify policy-related causes for nearly two-thirds of the difference between projecte…
Acknowledgments
- The authors thank Clifton Maze and Stephen Heffler at the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) for answering questions about CMS’s Medicare spending data. Johnny Chan provided excellent research assistance. Any remaining errors are those of the authors.
Notes
- 1 Dranove D , Garthwaite C , Ody C . Health spending slowdown is mostly due to economic factors, not structural change in the health care sector . Health Aff (Millwood) . 2014 ; 33 ( 8 ): 1399 – 40...
- 2 Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation . The facts on Medicare spending and financing [Internet]. Menlo Park (CA) : KFF ; 2014 Jul 28 [cited 2015 May 21 ]. (Fact Sheet). Available from: http://…
- 1 Dranove D , Garthwaite C , Ody C . Health spending slowdown is mostly due to economic factors, not structural change in the health care sector . Health Aff (Millwood) . 2014 ; 33 ( 8 ): 1399 – 40...
- 2 Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation . The facts on Medicare spending and financing [Internet]. Menlo Park (CA) : KFF ; 2014 Jul 28 [cited 2015 May 21 ]. (Fact Sheet). Available from: http://kff.org...
- 3 Levine M , Buntin M . Why has growth in spending for fee-for-service Medicare slowed? [Internet]. Washington (DC) : Congressional Budget Office ; 2013 Aug [cited 2015 May 21 ]. (CBO Working Paper...
- 4 White C , Cubanski J , Neuman T . How much of the Medicare spending slowdown can be e…