
Currently, Medicare covers a portion of the health care costs of over 61 million Americans, including approximately 5 million Latino Americans.
What percentage of the US population has Medicare?
Nonetheless, nearly 16% of its massive population of 39.5 million has Medicare, totaling about 6.3 million individuals. With Texas as the second most populous U.S. state, as of 2019, roughly 14% of Texas’ population has Medicare. By comparison, the state of Maine has over 25% of its population on Medicare.
What state has the most Medicare recipients?
The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation Headquarters: 185 Berry St., Suite 2000, San Francisco, CA 94107 | Phone 650-854-9400 Washington Offices and Barbara Jordan Conference Center: 1330 G …
How many Americans have no life insurance?
85,809,179 individuals were enrolled in Medicaid and CHIP in the 51 states that reported enrollment data for November 2021. 78,910,300 individuals were enrolled in Medicaid. 6,898,879 individuals were enrolled in CHIP.
How many Americans have no medical insurance?
Mar 16, 2022 · CMS has developed a new quick reference statistical summary on annual CMS program and financial data. CMS Fast Facts includes summary information on total program enrollment, utilization, expenditures, as well as total number of Medicare providers including physicians by specialty area. The download below will be updated as data become available.
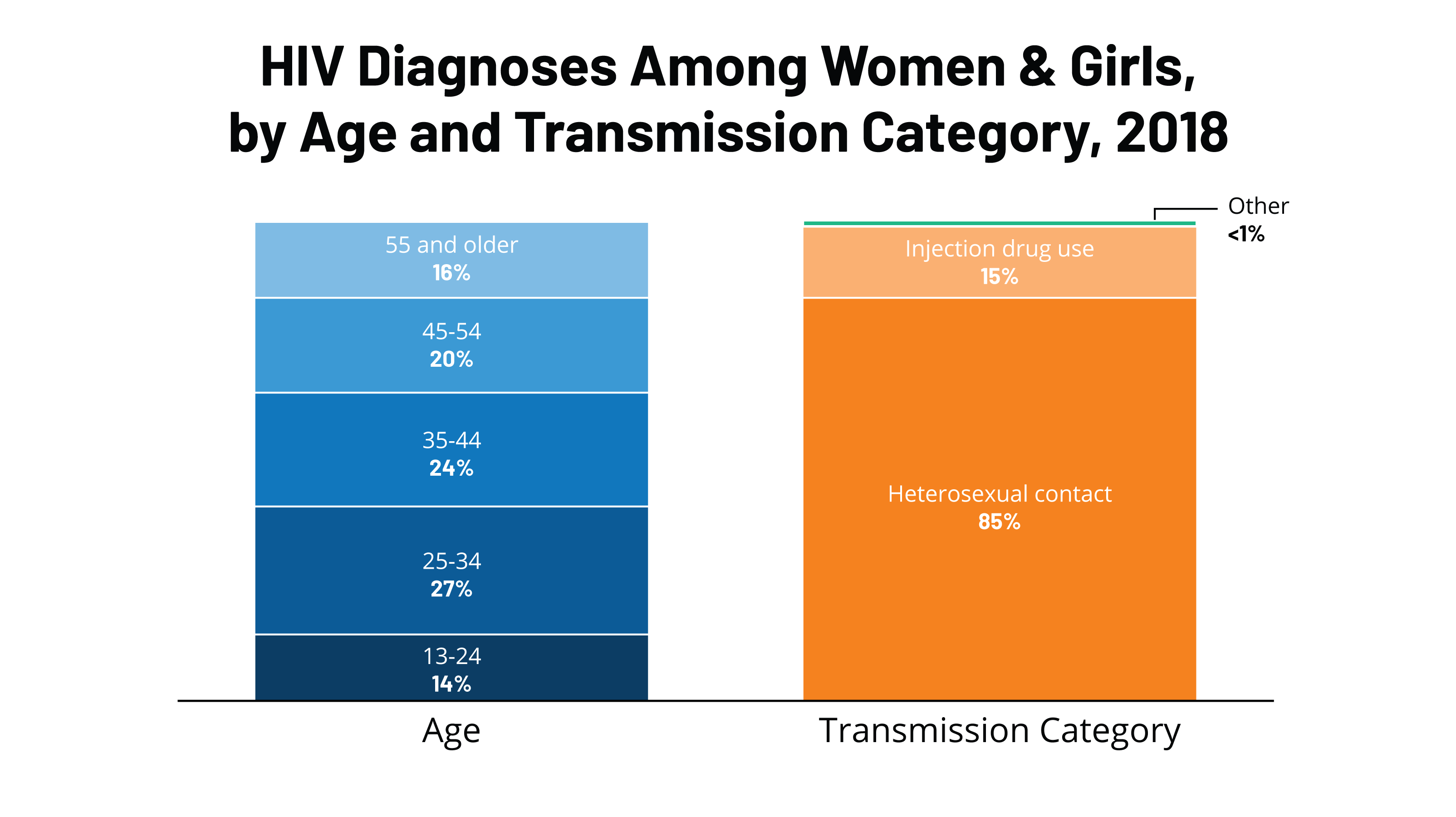
How many people in Texas have Medicare?
Nonetheless, nearly 16% of its massive population of 39.5 million has Medicare, totaling about 6.3 million individuals. With Texas as the second most populous U.S. state, as of 2019, roughly 14% of Texas’ population has Medicare. By comparison, the state of Maine has over 25% of its population on Medicare.
How many people are on medicare in 2020?
About 19 million people enrolled when Medicare first started. By 2020, that number grew to nearly 63 million. Overall, how many people per state enroll in Medicare?
What is Medicare health plan?
As often as monthly, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services keep tabs on trends in the Medicare population by: Generally meant by the term Medicare health plan are Medicare-approved health insurance products that works in addition to having Original Medicare.
What is Medicare count?
Counting Medicare enrollees per year and per month. Generally meant by the term Medicare health plan are Medicare-approved health insurance products that works in addition to having Original Medicare. As a means of getting benefits that can exceed Medicare, you can choose from Medicare health plans: Medicare Advantage (Part C) ...
How many Medicare Advantage subscribers are there in 2019?
Whereas in 2014, Medicare Advantage had about 16.2 million subscribers, by 2019 that number rose to nearly 23 million . As a whole, Medicare appears to be growing as the competition for benefits progresses.
What is the number to call for Medicare?
Dial (800) 950-0608 with your Medicare questions. With the aim of helping older Americans buy health insurance, Medicare became part of President Lyndon B. Johnson’s “Great Society” vision created in 1965. Although Medicare eligibility has nothing to do with income levels, it can provide healthcare both for Americans with disabilities as well as ...
Which states have the highest Medicare enrollment?
Overall, California, Florida and Texas have the highest number of people enrolled in Medicare. They are the only three states whose Medicare members exceed four million. Of course, California holding the title of most populous state translates to a higher Medicare population.
How many people have Medicare?
In 2018, according to the 2019 Medicare Trustees Report, Medicare provided health insurance for over 59.9 million individuals —more than 52 million people aged 65 and older and about 8 million younger people.
How is Medicare funded?
Medicare is funded by a combination of a specific payroll tax, beneficiary premiums, and surtaxes from beneficiaries, co-pays and deductibles, and general U.S. Treasury revenue. Medicare is divided into four Parts: A, B, C and D.
What is CMS in healthcare?
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), administers Medicare, Medicaid, the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP), the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA), and parts of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) ("Obamacare").
How much does Medicare cost in 2020?
In 2020, US federal government spending on Medicare was $776.2 billion.
What is Medicare and Medicaid?
Medicare is a national health insurance program in the United States, begun in 1965 under the Social Security Administration (SSA) and now administered by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). It primarily provides health insurance for Americans aged 65 and older, ...
What is a RUC in medical?
The Specialty Society Relative Value Scale Update Committee (or Relative Value Update Committee; RUC), composed of physicians associated with the American Medical Association, advises the government about pay standards for Medicare patient procedures performed by doctors and other professionals under Medicare Part B.
When did Medicare Part D start?
Medicare Part D went into effect on January 1, 2006. Anyone with Part A or B is eligible for Part D, which covers mostly self-administered drugs. It was made possible by the passage of the Medicare Modernization Act of 2003. To receive this benefit, a person with Medicare must enroll in a stand-alone Prescription Drug Plan (PDP) or public Part C health plan with integrated prescription drug coverage (MA-PD). These plans are approved and regulated by the Medicare program, but are actually designed and administered by various sponsors including charities, integrated health delivery systems, unions and health insurance companies; almost all these sponsors in turn use pharmacy benefit managers in the same way as they are used by sponsors of health insurance for those not on Medicare. Unlike Original Medicare (Part A and B), Part D coverage is not standardized (though it is highly regulated by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services). Plans choose which drugs they wish to cover (but must cover at least two drugs in 148 different categories and cover all or "substantially all" drugs in the following protected classes of drugs: anti-cancer; anti-psychotic; anti-convulsant, anti-depressants, immuno-suppressant, and HIV and AIDS drugs). The plans can also specify with CMS approval at what level (or tier) they wish to cover it, and are encouraged to use step therapy. Some drugs are excluded from coverage altogether and Part D plans that cover excluded drugs are not allowed to pass those costs on to Medicare, and plans are required to repay CMS if they are found to have billed Medicare in these cases.
Introduction
This report presents statistics on health insurance coverage in the United States based on information collected in the Current Population Survey Annual Social and Economic Supplement (CPS ASEC).
Highlights
In 2020, 8.6 percent of people, or 28.0 million, did not have health insurance at any point during the year.
America Counts Stories
Private Health Coverage of Working-Age Adults Drops From Early 2019 to Early 2021
Visualizations
Figure 1. Percentage of People by Type of Health Insurance Coverage and Change From 2018 to 2020
Tables
Table 1. Number and Percentage of People by Health Insurance Coverage Status and Type: 2018 to 2020
Health Insurance Historical Tables - HHI CPS (2017-2020)
HHI-01. Health Insurance Coverage Status and Type of Coverage--All Persons by Sex, Race and Hispanic Origin: 2017 to 2020
Health Insurance Detailed Tables
The Current Population Survey is a joint effort between the Bureau of Labor Statistics and the Census Bureau.
What is the federal Medicaid share?
The Federal share of all Medicaid expenditures is estimated to have been 63 percent in 2018. State Medicaid expenditures are estimated to have decreased 0.1 percent to $229.6 billion. From 2018 to 2027, expenditures are projected to increase at an average annual rate of 5.3 percent and to reach $1,007.9 billion by 2027.
What percentage of Medicaid beneficiaries are obese?
38% of Medicaid and CHIP beneficiaries were obese (BMI 30 or higher), compared with 48% on Medicare, 29% on private insurance and 32% who were uninsured. 28% of Medicaid and CHIP beneficiaries were current smokers compared with 30% on Medicare, 11% on private insurance and 25% who were uninsured.
What percentage of births were covered by Medicaid in 2018?
Other key facts. Medicaid Covered Births: Medicaid was the source of payment for 42.3% of all 2018 births.[12] Long term support services: Medicaid is the primary payer for long-term services and supports.
How much did the US spend on healthcare in 2016?
Health care costs rising far faster than inflation have been a major driver for health care reform in the United States. As of 2016, the US spent $3.3 trillion (17.9% of GDP), or $10,438 per person; major categories included 32% on hospital care, 20% on physician and clinical services, and 10% on prescription drugs.
How does the US health care system work?
The US health care delivery system unevenly provides medical care of varying quality to its population. In a highly effective health care system, individuals would receive reliable care that meets their needs and is based on the best scientific knowledge available. In order to monitor and evaluate system effectiveness, researchers and policy makers track system measures and trends over time. The US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) populates a publicly available dashboard called, the Health System Measurement Project (healthmeasures.aspe.hhs.gov), to ensure a robust monitoring system. The dashboard captures the access, quality and cost of care; overall population health; and health system dynamics (e.g., workforce, innovation, health information technology). Included measures align with other system performance measuring activities including the HHS Strategic Plan, the Government Performance and Results Act, Healthy People 2020, and the National Strategies for Quality and Prevention.
Why are uninsured people less likely to get care?
A 2007 study published in JAMA concluded that uninsured people were less likely than the insured to receive any medical care after an accidental injury or the onset of a new chronic condition. The uninsured with an injury were also twice as likely as those with insurance to have received none of the recommended follow-up care, and a similar pattern held for those with a new chronic condition. Uninsured patients are twice as likely to visit hospital emergency rooms as those with insurance; burdening a system meant for true emergencies with less-urgent care needs.
How many foreigners were in the US in 1998?
Of the 26.2 million foreign immigrants living in the US in 1998, 62.9% were non-U.S. citizens. In 1997, 34.3% of non-U.S. citizens living in America did not have health insurance coverage opposed to the 14.2% of native-born Americans who do not have health insurance coverage. Among those immigrants who became citizens, 18.5% were uninsured, as opposed to noncitizens, who are 43.6% uninsured. In each age and income group, immigrants are less likely to have health insurance. With the recent healthcare changes, many legal immigrants with various immigration statuses now are able qualify for affordable health insurance.
What is the federal government's responsibility for healthcare?
Essential regulation includes the licensure of health care providers at the state level and the testing and approval of pharmaceuticals and medical devices by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and laboratory testing. These regulations are designed to protect consumers from ineffective or fraudulent healthcare. Additionally, states regulate the health insurance market and they often have laws which require that health insurance companies cover certain procedures, although state mandates generally do not apply to the self-funded health care plans offered by large employers, which exempt from state laws under preemption clause of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act .
How can variation in health care delivery cause variation in outcomes?
The Dartmouth Atlas Project, for instance, reported that, for over 20 years, marked variations in how medical resources are distributed and used in the United States were accompanied by marked variations in outcomes. The willingness of physicians to work in an area varies with the income of the area and the amenities it offers, a situation aggravated by a general shortage of doctors in the United States, particularly those who offer primary care. The Affordable Care Act is anticipated to produce an additional demand for services which the existing stable of primary care doctors will be unable to fill, particularly in economically depressed areas. Training additional physicians would require some years.
What are high volume procedures?
The combination of high prices and high volume can cause particular expense; in the U.S., high-margin high-volume procedures include angioplasties, c-sections, knee replacements, and CT and MRI scans; CT and MRI scans also showed higher utilization in the United States.
What was the adjusted mortality rate for Medicare patients with CKD in 2013?
In 2013, adjusted mortality rates remained higher for Medicare patients with CKD (117.9/1,000) than for those without CKD (47.5/1,000); and these rates increased with CKD severity, although this gap narrowed during the period 2001 to 2013.
How many people died from kidney disease in 2013?
Each year, kidney disease kills more people than breast or prostate cancer. In 2013, more than 47,000 Americans died from kidney disease. 1.
How many children were treated for ESRD in 2013?
A total of 1,462 children in the United States began ESRD care in 2013, and 9,921 children were treated for ESRD on December 31, 2013. The most common initial ESRD treatment modality among children overall was hemodialysis (56 percent). The number of children listed for incident and repeat kidney transplant was 1,277 in 2013.
What is CKD in medical terms?
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Any condition that causes reduced kidney function over a period of time. Chronic kidney disease may develop over many years and lead to end-stage kidney (or renal) disease (ESRD). The five stages of CKD are:
How many people with CKD have kidney failure?
Almost half of individuals with CKD also have diabetes and/or self-reported cardiovascular disease (CVD). More than 661,000 Americans have kidney failure. Of these, 468,000 individuals are on dialysis, and roughly 193,000 live with a functioning kidney transplant.
How many kidney transplants were performed in 2013?
17,600 kidney transplants were performed in the United States in 2013. Less than one-third of the transplanted kidneys were from living donors in 2013. From 2012 to 2013, there was a 3.1 percent increase in the cumulative number of recipients with a functioning kidney transplant.
What are the risks of kidney failure?
If you have kidney disease, it increases your chances of having a stroke or heart attack. Major risk factors for kidney disease include diabetes, high blood pressure, and family history of kidney failure.

Overview
Medicare is a government national health insurance program in the United States, begun in 1965 under the Social Security Administration (SSA) and now administered by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). It primarily provides health insurance for Americans aged 65 and older, but also for some younger people with disabilitystatus as determined by the SSA, includ…
History
Originally, the name "Medicare" in the United States referred to a program providing medical care for families of people serving in the military as part of the Dependents' Medical Care Act, which was passed in 1956. President Dwight D. Eisenhowerheld the first White House Conference on Aging in January 1961, in which creating a health care program for social security beneficiaries was p…
Administration
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), administers Medicare, Medicaid, the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP), the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA), and parts of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) ("Obamacare"). Along with the Departments of Labor and Treasury, the CMS also implements the insurance reform provisions of the Health Insurance Portability an…
Financing
Medicare has several sources of financing.
Part A's inpatient admitted hospital and skilled nursing coverage is largely funded by revenue from a 2.9% payroll taxlevied on employers and workers (each pay 1.45%). Until December 31, 1993, the law provided a maximum amount of compensation on which the Medicare tax could be imposed annually, in the same way that the Social Security payroll tax operates. Beginning on January 1, …
Eligibility
In general, all persons 65 years of age or older who have been legal residents of the United States for at least five years are eligible for Medicare. People with disabilities under 65 may also be eligible if they receive Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) benefits. Specific medical conditions may also help people become eligible to enroll in Medicare.
People qualify for Medicare coverage, and Medicare Part A premiums are entirely waived, if the f…
Benefits and parts
Medicare has four parts: loosely speaking Part A is Hospital Insurance. Part B is Medical Services Insurance. Medicare Part D covers many prescription drugs, though some are covered by Part B. In general, the distinction is based on whether or not the drugs are self-administered but even this distinction is not total. Public Part C Medicare health plans, the most popular of which are bran…
Out-of-pocket costs
No part of Medicare pays for all of a beneficiary's covered medical costs and many costs and services are not covered at all. The program contains premiums, deductibles and coinsurance, which the covered individual must pay out-of-pocket. A study published by the Kaiser Family Foundation in 2008 found the Fee-for-Service Medicare benefit package was less generous than either the typical large employer preferred provider organization plan or the Federal Employees He…
Payment for services
Medicare contracts with regional insurance companies to process over one billion fee-for-service claims per year. In 2008, Medicare accounted for 13% ($386 billion) of the federal budget. In 2016 it is projected to account for close to 15% ($683 billion) of the total expenditures. For the decade 2010–2019 Medicare is projected to cost 6.4 trillion dollars.
For institutional care, such as hospital and nursing home care, Medicare uses prospective payme…