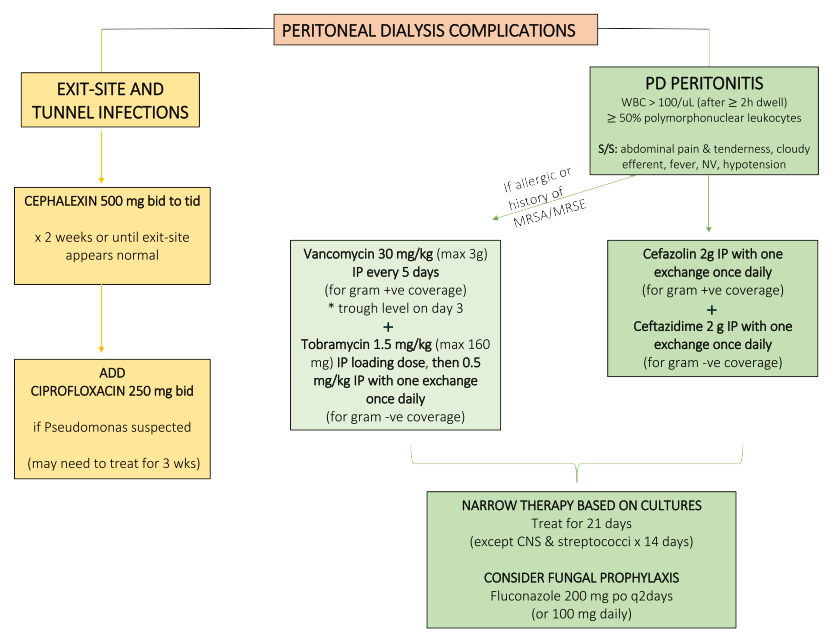
Kt = (ml/min*min) = ml V = ml Kt/V = dimensionless ratio NKF guidelines suggest a minimum Kt/V of 1.2 per hemodialysis session when three sessions per week are used in patients with no residual renal function based on cross sectional studies were increasing mortality has been associated with Kt/Vs of <1.2 and data from the HEMO trial.
Full Answer
What is Kt/V ratio in dialysis?
It is the ratio of urea clearance (K) multiplied by dialysis time (t) to the volume of water in your body. Kt/V values can be improved by either increasing blood flow rate through the dialyser, which increases urea clearance, or by increasing the duration of dialysis sessions.
What does Kt/V reveal about dialysis response in uremic pericarditis patients?
Discussion: In scenario 1, calculating Kt/V may reveal that subject is being underdialysed, despite a normal URR. This subject may need increased dialysis dose, and regular monitoring of adequacy of dialysis (Kt/V), and the regular protocol of dialysis advised to manage uremic pericarditis patient.
What are the KDOQI guidelines for thrice weekly hemodialysis?
KDOQI guidelines for thrice weekly hemodialysis KDOQI guidelines recommend that patients with residual kidney function of less than 2 ml/min on thrice a week hemodialysis should be prescribed at least 3 hours each dialysis session.[18]
When does Medicare coverage start after kidney dialysis?
If you’re eligible for Medicare only because of permanent kidney failure, your coverage usually can’t start until the fourth month of dialysis (also known as a “waiting period”).

How is KtV calculated in dialysis?
The Kt/V can be resolved from the predialysis to postdialysis urea nitrogen ratio (R), the weight loss (UF), session length in hours (t), and anthropometric or modeled volume (V) using the equation: KtV = In (R - 0.008 x t) + (4 - 3.5 x R) x 0.55 UF/V.
How is peritoneal dialysis prescription calculated?
In peritoneal dialysis, small-solute clearance (and, thus, the Kt/V) is determined by the total drain volume (dialysate plus ultrafiltration volume) multiplied by the concentration of the specific solute in the drained volume.
What is a good kt V for peritoneal dialysis?
Some centers advocate for a target Kt/V of 2.0 (the prior KDOQI guideline) to achieve an 'adequate' dose of peritoneal dialysis, as defined by small solute clearance.
What is Target kt V in dialysis?
On average, a Kt/V of 1.2 is roughly equivalent to a URR of about 63 percent. Thus, another standard of adequate dialysis is a minimum Kt/V of 1.2. The Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (KDOQI) group has adopted the Kt/V of 1.2 as the standard for dialysis adequacy.
What is PD calculator?
The online PD (Peritoneal Dialysis) Calculator is intended for use by clinicians for simulation, education, and training on modeling the dialysis dose (Kt/V) for different peritoneal dialysis prescription options. Modeling a PD dose is based on generalized formulas and assumptions derived from patient populations.
How is peritoneal dialysis efficiency measured?
Testing for Efficiency The peritoneal equilibration test—often called the PET—measures how much dextrose has been absorbed from a bag of infused dialysis solution and how much urea and creatinine have entered into the solution during a 4-hour dwell. The peritoneal transport rate varies from person to person.
How do you calculate standard KT V?
Derivation equation 1 is described in the article clearance (medicine). Equation 6 is then defined as standardized Kt/V (std Kt/V): const is 7×24×60×60 seconds, the number of seconds in a week.
How is KT v calculated with example?
As an example, if someone is infusing four 2 liter exchanges a day, and drains out a total of 9 liters per day, then they drain 9 × 7 = 63 liters per week. If the patient has an estimated total body water volume V of about 35 liters, then the weekly Kt/V would be 63/35, or about 1.8.
How is URR calculated?
How to calculate URR in dialysis?URR = [(Upre - Upost)/Upre] * 100%URR = [1 - (Upost/Upre)] * 100%
What is weekly Kt V?
Current clinical practice guidelines recommend that the dose of dialysis for hemodialysis schedules other than thrice weekly be measured by determination of the weekly standard Kt/V (stdKt/V) defined as the weekly urea generation rate factored by the average predialysis serum urea concentration during a week normalized ...
What factors influence V in KT v?
Dialysis dose as measured by Kt/V can be influenced by many factors, especially treatment time (TT) and blood flow rate (BFR), but also by dialysate flow, session interruption (hypotension or clotting), access functionality (stenosis and recirculation), needle size and placement, dialyzer characteristics and proper ...
What does Kt/V mean?
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. In medicine, Kt/V is a number used to quantify hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis treatment adequacy. K – dialyzer clearance of urea. t – dialysis time. V – volume of distribution of urea, approximately equal to patient's total body water.
What is the difference between Kt and V?
Kt/V is a measure of the dose of dialysis given in a single treatment where K is the dialyzer urea clearance , t is the total treatment time , and V is the total volume within the body that urea is distributed [68].
How does patient size affect dialysis?
In PD, we can increase the dose of dialysis by increasing the liters of dialysis used per day - either by increasing the fill volume or performing more exchanges per day.
When can Medicare start paying for dialysis?
It can start to pay on the 1st day of the 1st month for home dialysis—or at the 4th month of treatment for in-center. Starting Medicare on the 1st day of the 1st month can save thousands of dollars in out-of-pocket costs.
What is the Out of Pocket Cost Estimator?
Medicare has created a simple tool - The Out of Pocket Cost Estimator - to help you see how your coverage choices impact your costs. You can also compare your current costs with different coverage options.
When does Medicare close the window for home HD?
The date that closes the window is the 1st day of the 4th month of dialysis:
What is the ratio of urea clearance (K) multiplied by dialysis time (t) to?
It is the ratio of urea clearance (K) multiplied by dialysis time (t) to the volume of water in your body.
How to know if dialysis is adequate?
It is the ratio of urea clearance (K) multiplied by dialysis time (t) to the volume of water in your body. Kt/V values can be improved by either increasing blood flow rate through the dialyser, which increases urea clearance, or by increasing the duration of dialysis sessions.
How to improve Kt/V?
Kt/V values can be improved by either increasing blood flow rate through the dialyser, which increases urea clearance, or by increasing the duration of dialysis sessions. Probiotic Skin Therapy Helps Improve Eczema In Children, New Study Finds.
Is dialysis effective?
It is important to ensure that your dialysis sessions are consistently efficient. You may not immediately feel the harmful effects of waste materials building up in your body, but some symptoms can help you figure out if you are receiving inadequate dialysis.
What are the parameters of dialysis?
Clinical parameters including presence of uremic symptoms, and nutrition markers such as serum protein and albumin levels should also be monitored.[1,2,3] Combined assessment of a patient's laboratory markers and overall clinical status should be taken into consideration in the determination of adequacy and adjustment of the dialysis prescription.
What is the benefit of Kt/V calculation?
Advantage: Kt/V calculation assures clinicians, patients, insurance companies, and any concerned authority that adequate dialysis dose is being given to a patient. Also, it may help in timely intervention to modify dialysis dose prescription.
What is BUN in hemodialysis?
Post- dialysis BUN (mg/dL): BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen) measured from sample collected at the end of a session of hemodialysis (arbitrarily named as session A). If post-dialysis urea is being measured (and not BUN), then pre-dialysis urea (and not BUN), and urine urea (and not urine urea nitrogen) concentrations should be measured.
What is a Kt/Vurea?
Kt/Vurea('K' is dialyzer urea clearance, 't' is total dialysis session time, and 'V' is volume of distribution of urea which is approximately equal to total body water) is the most commonly used method of measurement of dialysis adequacy worldwide. The term 'Kt' (for urea) depicts volume of fluid completely cleared of urea in a single dialysis session. Kt/Vureawas developed by Frank Gotch and John Sargent.[4,5,6]
What is a single pool Kt/Vurea?
Single pool Kt/Vurea(spKt/Vurea): In this model, it is assumed that urea is in only one compartment or 'pool' of the body and that there is a linear decline in urea level during dialysis, and an immediate equilibration occurs between the blood and tissue compartments after dialysis. This is not true, as urea exists in intracellular and extracellular spaces (different compartments). Urea from intracellular space diffuses out into the extracellular space, but complete equilibration is not immediate as it is assumed in this model and takes 30 to 60 minutes after the end of dialysis session. As the test is performed before equilibration can occur, spKt/V is also referred to as 'non-equilibrated Kt/V'.[17] Please see Figure 1for understanding the basic concept of single pool Kt/Vurea.
How fast does a blood flow pump go on dialysis?
Towards the end of dialysis session, the blood flow pump is slowed to a speed of 100 ml/min for 15 seconds and then stopped, and blood sample is collected for post-dialysis BUN. This method helps in preventing hemodialysis access recirculation.[17]
What is significant residual kidney function?
Mathew A.T, Fishbane S, Obi Y and Kalantar-Zadeh K proposed that significant residual kidney function should be defined as >500 ml of urine output per day. They also proposed that RKF should be monitored regularly until urine volume is <100 mL/day or KRU (residual urea clearance by kidneys) is <2 mL/min/1.73m2.[9]