
The amount you could need to cover premiums and out-of-pocket prescription drug costs from age 65 on could be $130,000 if you’re a man and $146,000 if you’re a woman, according to one study. Sometimes, it comes as a surprise to older folks that Medicare is not free.
How much does the elderly spend on health care?
In 2010, healthcare spending amounted to $18,424 per person for people aged 65 and older – about five times as much as per-person spending for children ($3,628) and triple what was spent on working-age individuals ($6,125). Much of the elderly’s medical costs are paid for by the government.
How much does Medicare spend per capita by age?
Medicare per capita spending peaked at age 92 in 2000 ($9,557 in inflation-adjusted 2011 dollars), rising to age 96 by 2011 ($15,015 excluding Part D spending and $16,145 including Part D spending). Over time, the difference in Medicare per capita spending between beneficiaries ages 80 and older and younger beneficiaries has widened.
How much do Medicare beneficiaries spend on Long-Term Care?
A significant portion of spending for all Medicare beneficiaries was on long-term care, with people living in the community (as opposed to a nursing home) spending only $4,519. Around 5 percent of Original Medicare beneficiaries were institutionalized in 2016, and had out-of-pocket spending costs that averaged more than $23,000.
Is Medicare expensive for seniors?
Many seniors mistakenly believe that because Medicare provides universal coverage, it’s inexpensive. However, Medicare is costly, if not prohibitive, for the half of Americans over age 65 with incomes below $29,650 in 2019, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation. KFF also points out that one in four was living on less than $17,000.
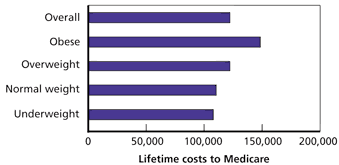
How much do the elderly spend on healthcare?
U.S. households led by someone who is 65 or older spend an average of $6,668 a year on health care, according to the federal Bureau of Labor Statistics' latest data on consumer spending, which is for 2020.
What percentage of seniors use Medicare?
Most Americans are automatically entitled, on reaching age 65, to health insurance benefits under the Medicare program. Today almost 96 percent of the nation's elderly have Medicare coverage.
How much do people spend on Medicare?
Medicare Beneficiaries' Spending for Health Care People covered by traditional Medicare paid an average of $6,168 for health care in 2018. They spent almost half of that money (47 percent) on Medicare or supplemental insurance premiums.
How much does the government spend per person on Medicare?
Medicare spending per person has also grown, increasing from $5,800 to $15,300 between 2000 and 2021 – or 4.7% average annual growth over the 21-year period. The influx of the Baby Boomer generation added many relatively younger, healthier people to the Medicare population beginning in 2011.
Who uses the most Medicare?
The majority (83%) of Medicare beneficiaries are ages 65 and older, while 17 percent are under age 65 and qualify for Medicare because of a permanent disability. However, a much larger share of black (31%) and Hispanic beneficiaries (23%) than white beneficiaries (14%) are under age 65 and living with disabilities.
Why is Medicare Advantage being pushed so hard?
Advantage plans are heavily advertised because of how they are funded. These plans' premiums are low or nonexistent because Medicare pays the carrier whenever someone enrolls. It benefits insurance companies to encourage enrollment in Advantage plans because of the money they receive from Medicare.
Is Medicare free at age 65?
You are eligible for premium-free Part A if you are age 65 or older and you or your spouse worked and paid Medicare taxes for at least 10 years. You can get Part A at age 65 without having to pay premiums if: You are receiving retirement benefits from Social Security or the Railroad Retirement Board.
How much does the average US citizen spend on healthcare?
How Much Does the United States Spend on Healthcare? The United States has one of the highest costs of healthcare in the world. In 2020, U.S. healthcare spending reached $4.1 trillion, which averages to over $12,500 per person.
What percentage of the budget is Medicare?
Key Facts. Medicare is the second largest program in the federal budget: 2022 Medicare expenditures, net of offsetting receipts, totaled $767 billion — representing 13 percent of total federal spending.
How much did the US spend on Medicare in 2020?
$829.5 billionMedicare spending totaled $829.5 billion in 2020, representing 20% of total health care spending. Medicare spending increased in 2020 by 3.5%, compared to 6.9% growth in 2019. Fee-for-service expenditures declined 5.3% in 2020 down from growth of 2.1% in 2019.
What does Medicare spend the most on?
Medicare plays a major role in the health care system, accounting for 20 percent of total national health spending in 2017, 30 percent of spending on retail sales of prescription drugs, 25 percent of spending on hospital care, and 23 percent of spending on physician services.
Does everyone pay for Medicare?
Everyone pays for Part B of Original Medicare. In 2020, the standard premium is $144.60/month for those making no more than $87,000 per year ($174,000 per year for married couples filing jointly). For 2020, the threshold for having to pay higher premiums based on income increased.
How much did Medicare spend in 2014?
Medicare spending alone totaled $618.7 billion in 2014. A group of researchers led by economist Mariacristina De Nardi of the Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago sought to better understand how much money goes toward medical care for Americans aged 65 and older.
Who pays for the elderly?
Much of the elderly’s medical costs are paid for by the government. Almost all Americans who are 65 years old or older are eligible for Medicare, the federal government’s health insurance program.
What is the 2015 Medicare report?
Their 2015 report, titled “Medical Spending of the U.S. Elderly,” was completed for the National Bureau of Economic Research as part of the agency’s working paper series. The report is based on data collected between 1996 and 2010 through the Medicare Current Beneficiary Survey. Some of their key findings are:
What percentage of the US population is senior citizen?
Senior citizens made up 13 percent of the U.S. population but accounted for 34 percent of healthcare-related spending in 2010, a report from the U.S. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services shows.
What will happen to the elderly population in 2050?
By 2050, the elderly population – especially those who are 85 years old and older – is predicted to start growing at a faster rate than the working age population. Such a dynamic could have significant implications for the U.S. in numerous areas beyond social security. One area that will be impacted most is health care.
How many people will be 65 in 2050?
In the year 2050, there will be 83.7 million people in the United States who are 65 years old or older, according to estimates from the U.S. Census Bureau. That’s nearly twice as many senior citizens as there were in 2012. By 2050, the elderly population – especially those who are 85 years old and older – is predicted to start growing ...
How much did Medicare spend in 2011?
Average Medicare per capita spending in 2011 more than doubled between age 70 ($7,566) and age 96 ($16,145). The increase in Medicare per capita spending as beneficiaries age can be partially, but not completely, explained by the high cost of end-of-life care.
When did Medicare per capita increase?
Between 2000 and 2011, Medicare per capita spending grew faster for beneficiaries ages 90 and older than for younger beneficiaries over age 65, both including and excluding spending on the Part D prescription drug benefit beginning in 2006.
Why is the analysis focusing on Medicare beneficiaries over age 65 rather than younger adults who qualify for Medicare?
The analysis focuses on Medicare beneficiaries over age 65 rather than younger adults who qualify for Medicare because of a permanent disability to develop a better understanding of the relationship between Medicare spending and advancing age. This study examines patterns of Medicare spending among beneficiaries in traditional Medicare rather ...
What percentage of Medicare beneficiaries were enrolled in 2011?
Because we lack comparable data for the 25 percent of beneficiaries enrolled in Medicare Advantage in 2011, it is not possible to assess whether patterns of service use and spending in traditional Medicare apply to the Medicare population overall. More information about the data, methods, and limitations can be found in the Methodology.
Is Medicare spending data available for all people?
The analysis excludes beneficiaries who are age 65 because some of these beneficiaries are enrolled for less than a full year; therefore, a full year of Medicare spending data is not available for all people at this year of age. The analysis focuses on Medicare beneficiaries over age 65 rather than younger adults who qualify for Medicare because ...
Will population aging affect health care?
According to the Congressional Budget Office, population aging is expected to account for a larger share of spending growth on the nation’s major health care programs through 2039 than either “excess spending growth” or subsidies for the coverage expansions provided under the Affordable Care Act. 2. To inform discussions about Medicare’s role in ...
Does Medicare increase as you age?
As the U.S. population ages, the increase in the number of people on Medicare and the aging of the Medicare population are expected to increase both total and per capita Medicare spending. The increase in per capita spending by age not only affects Medicare, but other payers as well.
How much does Medicare pay for outpatient therapy?
After your deductible is met, you typically pay 20% of the Medicare-approved amount for most doctor services (including most doctor services while you're a hospital inpatient), outpatient therapy, and Durable Medical Equipment (DME) Part C premium. The Part C monthly Premium varies by plan.
What is Medicare Advantage Plan?
A Medicare Advantage Plan (Part C) (like an HMO or PPO) or another Medicare health plan that offers Medicare prescription drug coverage. Creditable prescription drug coverage. In general, you'll have to pay this penalty for as long as you have a Medicare drug plan.
How much is coinsurance for 61-90?
Days 61-90: $371 coinsurance per day of each benefit period. Days 91 and beyond: $742 coinsurance per each "lifetime reserve day" after day 90 for each benefit period (up to 60 days over your lifetime) Beyond lifetime reserve days: all costs. Part B premium.
What happens if you don't buy Medicare?
If you don't buy it when you're first eligible, your monthly premium may go up 10%. (You'll have to pay the higher premium for twice the number of years you could have had Part A, but didn't sign up.) Part A costs if you have Original Medicare. Note.
Do you pay more for outpatient services in a hospital?
For services that can also be provided in a doctor’s office, you may pay more for outpatient services you get in a hospital than you’ll pay for the same care in a doctor’s office . However, the hospital outpatient Copayment for the service is capped at the inpatient deductible amount.
Does Medicare cover room and board?
Medicare doesn't cover room and board when you get hospice care in your home or another facility where you live (like a nursing home). $1,484 Deductible for each Benefit period . Days 1–60: $0 Coinsurance for each benefit period. Days 61–90: $371 coinsurance per day of each benefit period.
How much does a female Medicare beneficiary spend on health insurance?
Female Medicare beneficiaries spent a slightly higher average portion of self-reported income on health coverage and out-of-pocket costs than their male counterparts (spending $5,748 versus $5,104 spent by men), although this was not the case for those under age 65 who are enrolled in Medicare because of disability.
How much did Medicare cost in 2016?
In 2016, Medicare enrollees who reported being in poor health spent $6,384 in premiums and out-of-pocket health costs, while those who reported being in excellent or good health had average costs of $4,715.
How much did Medicare pay out of pocket in 2016?
A: According to a Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF) analysis of Medicare Current Beneficiary Survey (MCBS), the average Medicare beneficiary paid $5,460 out-of-pocket for their care in 2016, including premiums as well as out-of-pocket costs when health care was needed.
Does Medicare cover long term care?
In addition to cost sharing (deductibles, co-pays and coinsurance), beneficiaries have to pay out-of-pocket for expenses Medicare doesn’t cover, such as long-term care and dental services. According to the KFF analysis, the amount Medicare beneficiaries paid for covered and non-covered care decreased slightly from 2013 and 2016, ...
Is there a deductible for Medicare Part A 2020?
The Part A deductible and coinsurance also increased slightly in 2020, as did the premium for Part A that applies to people who don’t have enough work history (or a spouse with enough work history) to qualify for premium-free Medicare Part A.
How much does Medicare cost when you are 65?
From then on it's a steady increase, however, with costs rising to over $11,000 per year when you're over 65 years old. The costs of your care may be mostly covered by private insurance or Medicare, but not all costs are always covered and an unexpected bill can have devastating effects on your finances.
How much does a woman spend on health care?
During time period of age 18 to 44, health spending for females is 84% higher than men for years. Yes, much of this is due to the expense of childbirth, but from age 44 to 64 spending for women is 24% higher than for men and even at age 65+ spending for women is 8% higher.
How much will healthcare cost if inflation is 3%?
And that is if medical costs rise as the same rate as inflation. If medical costs rise at 3% more than inflation, your healthcare will cost over $2MM, the vast majority of which will take place after the age of 45. Even if your insurance company or Medicare covers most of that bill, the typical American can still be on the hook for ...
What does high healthcare cost mean?
Either way, high healthcare costs mean high spending for someone. Not only that, but even with the best health insurance, senior citizens are often hit with expensive co-pays or need drugs that their plans won't cover. These unexpected and large expenses can often wreck one's finances and result in bankruptcy.
Is healthcare evenly distributed?
Healthcare costs are not evenly distributed. You could be among the tragically unlucky with much higher costs. But not only that, but healthcare spending varies substantially by gender and demographic. At each stage of life, health care spending for women is substantially higher than for men.
Does healthcare go up as you age?
It turns out as you age , your annual healthcare costs go up a lot and despite having insurance you may be on the hook for copays, deductibles, and all sorts of things that aren't actually covered. The MEPS data set shows the average spending per person in the United States based on their age group.
Does Medicare cover seniors?
Despite the existence of Medicare insurance for seniors, it doesn't cover all costs and healthcare can be extremely expensive, especially as you age. In this analysis, we decide to look at the most recent data on how healthcare spending increases as you age. The goal of this is for people to understand just how much higher healthcare costs are ...
Medicare Covers Medically Necessary Home Health Services
Medicare does not usually cover the cost of non-medical home care aides if that is the only type of assistance that a senior needs.
Medicare Advantage May Offer More Comprehensive Coverage
Private insurance companies run Medicare Advantage. Those companies are regulated by Medicare and must provide the same basic level of coverage as Original Medicare. However, they also offer additional coverage known as “supplemental health care benefits.”
