How much does it cost to administer Medicare?
administrative costs are in the 20 to 25 percent range — or more.1 That assertion is nearly always followed by a policy recommendation: Switch everyone to a government-financed health care system — or just put everyone in Medicare — and the country will save so much in administrative costs that it can cover all of the 46
Would 'Medicare for all' save billions in administrative costs?
The latest trustees’ report indicates Medicare’s administrative expenditures are 1 percent of total Medicare spending, while the latest NHEA indicates the figure is 6 percent. The debate about Medicare’s administrative expenditures, which emerged several years ago, reflects widespread confusion about these data.
How much does health insurance administration cost per person?
The combined administrative expenses of the intermediaries and Government for Medicare ranged from 4.6 percent to 5.2 percent of ex- penditures from fiscal years 1967 to 1973. The 1967 administrative cost data, however, include some start-up costs incurred in 1965 and 1966.
What is a Medicare fee schedule?
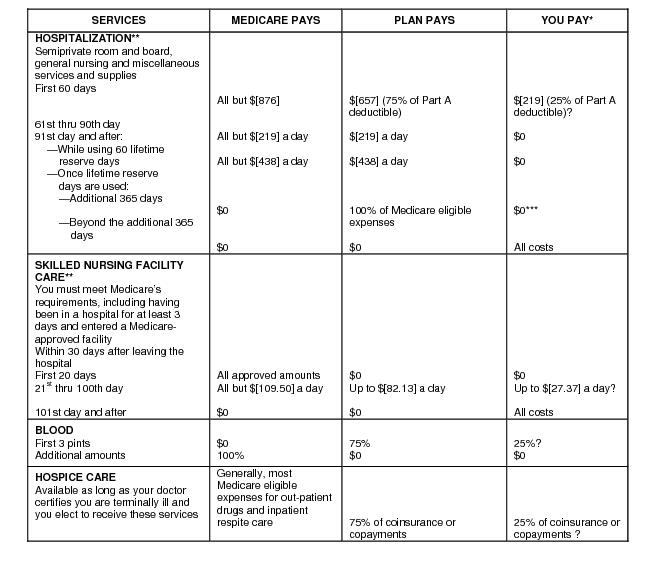
If you buy Part A, you'll pay up to $499 each month in 2022. If you paid Medicare taxes for less than 30 quarters, the standard Part A premium is $499. If you paid Medicare taxes for 30-39 quarters, the standard Part A premium is $274. Part A hospital inpatient deductible and coinsurance: You pay: $1,556 deductible for each benefit period

What percentage of Medicare is administrative expenditure?
The latest trustees’ report indicates Medicare’s administrative expenditures are 1 percent of total Medicare spending, while the latest NHEA indicates the figure is 6 percent. The debate about Medicare’s administrative expenditures, which emerged several years ago, reflects widespread confusion about these data. Critics of Medicare argue that the official reports on Medicare’s overhead ignore or hide numerous types of administrative spending, such as the cost of collecting taxes and Part B premiums. Defenders of Medicare claim the official statistics are accurate. But participants on both sides of this debate fail to cite the official documents and do not analyze CMS’s methodology. This article examines controversy over the methodology CMS uses to calculate the trustees’ and NHEA’s measures and the sources of confusion and ignorance about them. It concludes with a discussion of how the two measures should be used.
What is CMS in Medicare?
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) annually publishes two measures of Medicare’s administrative expenditures. One of these appears in the reports of the Medicare Boards of Trustees and the other in the National Health Expenditure Accounts (NHEA).
How much does Medicare pay for outpatient therapy?
After your deductible is met, you typically pay 20% of the Medicare-approved amount for most doctor services (including most doctor services while you're a hospital inpatient), outpatient therapy, and Durable Medical Equipment (DME) Part C premium. The Part C monthly Premium varies by plan.
What is Medicare Advantage Plan?
A Medicare Advantage Plan (Part C) (like an HMO or PPO) or another Medicare health plan that offers Medicare prescription drug coverage. Creditable prescription drug coverage. In general, you'll have to pay this penalty for as long as you have a Medicare drug plan.
How much is coinsurance for days 91 and beyond?
Days 91 and beyond: $742 coinsurance per each "lifetime reserve day" after day 90 for each benefit period (up to 60 days over your lifetime). Beyond Lifetime reserve days : All costs. Note. You pay for private-duty nursing, a television, or a phone in your room.
How much is coinsurance for 61-90?
Days 61-90: $371 coinsurance per day of each benefit period. Days 91 and beyond: $742 coinsurance per each "lifetime reserve day" after day 90 for each benefit period (up to 60 days over your lifetime) Beyond lifetime reserve days: all costs. Part B premium.
What happens if you don't buy Medicare?
If you don't buy it when you're first eligible, your monthly premium may go up 10%. (You'll have to pay the higher premium for twice the number of years you could have had Part A, but didn't sign up.) Part A costs if you have Original Medicare. Note.
Does Medicare cover room and board?
Medicare doesn't cover room and board when you get hospice care in your home or another facility where you live (like a nursing home). $1,484 Deductible for each Benefit period . Days 1–60: $0 Coinsurance for each benefit period. Days 61–90: $371 coinsurance per day of each benefit period.
Do you pay more for outpatient services in a hospital?
For services that can also be provided in a doctor’s office, you may pay more for outpatient services you get in a hospital than you’ll pay for the same care in a doctor’s office . However, the hospital outpatient Copayment for the service is capped at the inpatient deductible amount.
How are administrative costs calculated?
Administrative costs are calculated using faulty arithmetic. But most important, because Medicare patients are older, they are substantially sicker than the average insured patient — driving up the denominator of such calculations significantly.
What are the government agencies that administer Medicare?
First, other government agencies help administer the Medicare program. The Internal Revenue Service collects the taxes that fund the program; the Social Security Administration helps collect some of the premiums paid by beneficiaries (which are deducted from Social Security checks); the Department of Health and Human Services helps to manage accounting, auditing, and fraud issues and pays for marketing costs, building costs, and more. Private insurers obviously don't have this kind of outside or off-budget help. Medicare's administration is also tax-exempt, whereas insurers must pay state excise taxes on the premiums they charge; the tax is counted as an administrative cost. In addition, Medicare's massive size leads to economies of scale that private insurers could also achieve, if not exceed, were they equally large.
Is Medicare more expensive than private insurance?
And by that measure, even with all the administrative advantages Medicare has over private coverage, the program's administrative costs are actually significantly higher than those of private insurers.
Is Medicare tax exempt from state taxes?
Private insurers obviously don't have this kind of outside or off-budget help. Medicare's administration is also tax-exempt, whereas insurers must pay state excise taxes on the premiums they charge; the tax is counted as an administrative cost.
Components of administrative costs
The main components of administrative costs in the U.S. health care system include BIR costs and hospital or physician practice administration. 4 The first category, BIR costs, is part of the administrative overhead that is baked into consumers’ insurance premiums and providers’ reimbursements.
Billing and insurance-related costs
Many studies of administrative costs limit their scope to BIR costs. The BIR component of administration is most relevant to systemwide reforms that seek to reduce the expenses related to claims processing, billing rates, or health insurance.
Excess administrative costs
While U.S. administrative care spending is indisputably higher than that of other comparable countries, it’s unclear how much of the difference is excess and how much of that excess could be trimmed.
Administrative costs for payers
Within the U.S. system, the share of expenditures that are attributable to administrative costs varies greatly by payer. The BIR costs for traditional Medicare and Medicaid hover around 2 percent to 5 percent, while those for private insurance is about 17 percent.
Administrative costs for health care providers
A number of studies have focused on the administrative costs borne by providers. Beyond BIR expenses, hospitals, physician practices, and other health care institutions house departments that are complementary to clinical services such as medical libraries, public relations, and accounting.
Lower administrative costs in single-payer and multipayer systems
Although administrative costs contribute to the high expenditures in the United States, they are not the primary reason for the health care spending gap.
Conclusion
Although estimates vary, a large body of evidence shows that the United States is spending about twice as much as needed on the administration of health care. Other nations enjoy world-class health care systems while spending a fraction of what the United States does on governance, billing, and insurance.
How does treatment coded affect insurance?
How a patient’s treatment is coded can make a huge difference in the amount insurance companies pay. For example, Hammerstein said, if a patient comes in because of heart failure and the visit is coded as an acute exacerbation of the condition, the payment is significantly higher than if the visit is simply coded as heart failure.
How much has the administration cost increased since 1999?
They also found there had been a 3.2% increase in U.S. administrative costs since 1999, most of which was ascribed to the expansion of Medicare and Medicaid managed-care plans.
How much did the government spend on administration in 2017?
(Reuters Health) - U.S. insurers and providers spent more than $800 billion in 2017 on administration, or nearly $2,500 per person - more than four times the per-capita administrative costs in Canada’s single-payer system, a new study finds.
What do private insurers do?
In addition, private insurers create provider networks, which is where they determine which doctors will offer which services under each plan and negotiate reimbursement rates. They also review which drugs will be most effective and affordable.
What is administrative cost?
Administrative costs are the expenses incurred by medical insurers that are not strictly medical, such as marketing, customer service, billing, claims review, quality assurance, information technology and profits. Is the gap between private and public health insurance providers’ administrative costs really that high?
Why are administrative expenses higher in commercial markets?
Historically, administrative expenses were much higher in the commercial market because insurers did a lot of underwriting, or using the health status of individuals or groups to determine their premiums. The Affordable Care Act was designed to curb that spending.
Does Medicare piggyback on Social Security?
But because much of Medicare piggybacks off Social Security, other administrative costs such as enrollment, payment and keeping track of patients are left to the Social Security system.
Is Medicare Advantage competitive with Medicare?
Glied pointed out that private Medicare Advantage plans are "pretty competitive with traditional Medicare," but also tend to operate at higher administrative costs. "They bring costs down in other ways but they have to use administrative spending to do that," Glied said.
Is Medicare a single payer?
Experts told us that a single-payer system for the United States would have lower administrative costs than today’s private insurance, but it likely wouldn’t be able to achieve administrative costs as low as the existing Medicare program.