Full Answer
How will Medicare for all affect private insurance companies?
If Medicare for All becomes the new American healthcare system, many healthcare industry professionals could face major changes. The impact of Medicare for All on private insurance companies would be the most drastic, aggressive change by far. Many of the proposed Medicare for All bills advocate for a complete elimination of private insurers.
How will Medicare changes affect the future of the healthcare industry?
But decreases and changes in payment policy could cause changes to the business of health care as hospitals, doctors, nurses and others adjust to lower payment rates and salaries. Universal Medicare-like payment rates would almost certainly cause some major disruptions, like hospital closings.
What would be the negative impact of Medicare for all?
However, a negative impact of Medicare for All would be that a single-payer system would almost certainly decrease profit margins of hospitals across the country.
Will Medicare for all change Medicare as we know it?
If enacted, Medicare for All would change Medicare as we know it, which will have a huge effect on the roughly 168 million Americans who are currently enrolled in Medicare. As a Medicare beneficiary, you may be wondering: how exactly will Medicare for All affect my coverage?

What are the downsides of Medicare for All?
Cons of Medicare for All:Providers can choose only private pay options unless mandated differently.Doesn't solve the shortage of doctors.Health insurance costs may not disappear.Requires a tax increase.Shifts costs of employer coverage.
How would doctors be affected by Medicare for All?
If, as studies suggest, Medicare for All would free up roughly 5% of doctors' work hours currently spent on billing, allowing them to increase patient care, per-physician revenue could rise by between $39,816 and $157,412 annually.
How are insurance companies paid by Medicare?
The plans receive some funding through monthly plan premiums, but most of the money comes from Medicare. The private insurance companies that offer the plans receive a payment each month from Medicare. This covers the costs of Medicare parts A and B for each beneficiary.
How Medicare for All would hurt the economy?
The real trouble comes when Medicare for all is financed by deficits. With government borrowing, universal health care could shrink the economy by as much as 24% by 2060, as investments in private capital are reduced.
What are the disadvantages of free healthcare?
Disadvantages of universal healthcare include significant upfront costs and logistical challenges. On the other hand, universal healthcare may lead to a healthier populace, and thus, in the long-term, help to mitigate the economic costs of an unhealthy nation.
Why do so many doctors oppose single-payer health care?
What were their concerns? The top one is really their own pay. And the second one is their autonomy in the practice of medicine. Going back to the 1910s and also in the 1940s, there's this fear that if there is a universal public insurance plan, doctors are going to get paid less.
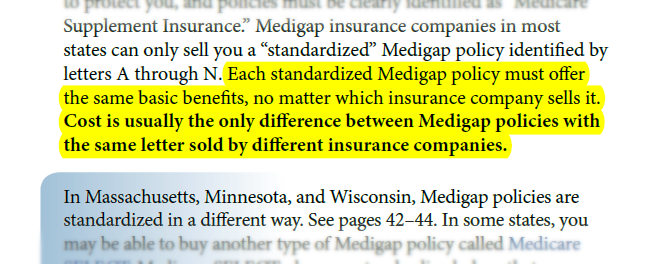
What is the biggest disadvantage of Medicare Advantage?
Medicare Advantage can become expensive if you're sick, due to uncovered copays. Additionally, a plan may offer only a limited network of doctors, which can interfere with a patient's choice. It's not easy to change to another plan. If you decide to switch to a Medigap policy, there often are lifetime penalties.
What happens when Medicare runs out of money?
It will have money to pay for health care. Instead, it is projected to become insolvent. Insolvency means that Medicare may not have the funds to pay 100% of its expenses. Insolvency can sometimes lead to bankruptcy, but in the case of Medicare, Congress is likely to intervene and acquire the necessary funding.
Do doctors lose money on Medicare patients?
Summarizing, we do find corroborative evidence (admittedly based on physician self-reports) that both Medicare and Medicaid pay significantly less (e.g., 30-50 percent) than the physician's usual fee for office and inpatient visits as well as for surgical and diagnostic procedures.
Why is universal health care bad for the economy?
Even under universal coverage, some may decline coverage because their costs are too high. These costs include out-of-pocket costs for premiums, time spent filling out forms, and the availability of information about health care coverage.
What are the pros and cons of free healthcare?
Here are a few pros and cons of universal healthcare.PRO: Make It Easier for Patients to Seek Treatment. ... CON: Doctors Have Less Flexibility in Negotiating Rates. ... Must Read: What Does Universal Healthcare Means for Medical Practices. ... PRO: It Could Increase Demand for Medical Services.More items...
What would happen if we had universal healthcare?
Most agree that if we had universal healthcare in America, we could save lives. A study from Harvard researchers states that not having healthcare causes around 44,789 deaths per year. 44,789 deaths per year means that there is a 40% increased risk of death for people who are uninsured.
The Basics of Medicare for All
The idea behind Medicare for All is simple: instead of having the freedom to choose between Medicare and private health insurance, citizens would receive comprehensive health services from the government.
How Medicare for All Would Affect Private Insurance Companies
If Medicare for All was implemented tomorrow, its effects would be far-reaching. Though the plan wouldn’t touch healthcare providers, it would effectively nationalize the healthcare insurance industry.
How Likely Is Joe Biden to Pass Medicare for All?
Though Biden is a staunch supporter of public healthcare, it’s unlikely that he’ll support Medicare for All. In March of last year, he criticized the plan’s price tag and suggested he might veto it in the future.
What would eliminate many of the elements associated withour current Medicare system?
dental care. vision care. hearing care. prescription drugs. Medicarefor All, which would be run and funded by the government and available to everysingle American citizen, would eliminate many of the elements associated withour current Medicare system, such as: private insurance plans. age requirements for enrollment.
How many people are in Medicare for All?
If enacted, Medicare for All would change Medicare as we know it, which will have a huge effect on the roughly 168 million Americans who are currently enrolled in Medicare.
How many people are in Medicare Advantage 2019?
In 2019, 34 percent, or nearly one third of all Medicare recipients, were enrolled in a Medicare Advantage plan. The elimination of this type of plan would impact a huge portion of beneficiaries, some of whom enjoy Medicare Advantage simply because it is a private option.
What is Medicare Advantage Plan?
Medicare Advantage plans are Medicare plansthat are sold by private insurance companies contracted with Medicare. Withoutprivate insurance under Medicare for All, Medicare Part C would no longer be anoption. In 2019, 34 percent, or nearly one third of all Medicare recipients, were enrolled in a Medicare Advantage plan.
What is the ACA?
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act or simply the Affordable Care Act (ACA), often referred to as Obamacare, was designed to create affordable healthcare options for more Americans. As an alternative to Medicare for All, the changes according to Joe Biden, to the ACA would include:
What is Joe Biden's alternative to Medicare?
Joe Biden’s alternative to Medicare for All includes an expansion of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) that was enacted under President Obama in 2010. These changes would not impact Medicare beneficiaries in the same way that Medicare for All would.
Is Medicare for all a tax financed system?
The Medicare for All proposal calls for a healthcare system similar to Canada through an expansion of Medicare. This expansion would include all necessary healthcare services, with no up-front cost to beneficiaries. Like most other tax-financed, single-payer systems, the cost of all healthcare services would be paid for through taxes.
How would Medicare for All affect you?
Under a plan proposed by Senator Bernie Sanders of Vermont on Wednesday, all Americans would get government-funded health insurance: “Medicare for all.”. What that would mean for you as a consumer depends on whether you currently have insurance, and if so how you’re covered.
What would happen if people with Medicaid were insured?
People insured through work would have new taxes, but no more premiums. People with Medicaid would have more choices, but possibly higher taxes . People currently with Medicare would have more generous coverage. The uninsured would all get health care.
How many people are covered by Medicare?
Medicare is now available to about 61 million people age 65 and older and to some younger people with disabilities. Coverage for these people would become more generous because the Sanders bill would expand to cover dental, vision and hearing aids, which are not covered under current law.
Why would private insurance companies be eliminated?
Because everyone would eventually get insurance from Medicare, private insurance companies would essentially be eliminated. The bill would bar employers from offering private insurance once the new system becomes universal. The bill does establish a program to help the industry’s workers transition to new careers.
How many people would get Medicare if they bought Obamacare?
The 21 million people who currently buy their own coverage, either in the Obamacare marketplaces or directly from insurance companies, would instead get Medicare. The Affordable Care Act exchanges would be eliminated.
Does Medicaid pay for nursing homes?
The part of Medicaid that currently pays for institutional long-term care, like nursing homes, would remain in place. That means that some Medicaid beneficiaries would be enrolled in both programs. Other kinds of long-term care, such as home-based services, would become part of the new Medicare system.
Does the Medicare bill cover the industry?
Insurance would be allowed to cover services that are not part of the Medicare system, but they would probably be marginal, since the bill establishes a robust set of Medicare benefits.
What percentage of voters believe Medicare is for all?
A January survey by the Kaiser Family Foundation found 55 percent of voters interpreted the phrase "Medicare for All" to mean a public option they can turn to if they don't like their private plans, rather than a single-payer, government-run program that covers everybody.
Who endorsed single payer health care?
At the time Harris endorsed single-payer health care as a presidential contender, it was easy to envision much of the Democratic field doing the same. Several rivals, including Sens. Cory Booker, Kirsten Gillibrand and Elizabeth Warren had also co-sponsored the Sanders bill and continue to do so now.
Did Harris run for single payer?
Harris made a decision early in the race to run on single-payer Medicare for All, specifically a bill by Sen. Bernie Sanders, I-Vt., that would effectively replace existing private health insurance plans with a souped-up version of Medicare that covers more than the current program and requires no premiums or deductibles.
Does the Medicare bill get rid of insurance?
As it relates to Medicare... TAPPER: But the bill gets rid of insurance. HARRIS: But — no, no, no, no, it does not get rid of insurance. It does not get rid of insurance. Her answer is technically accurate if you squint at it, but it's also likely to confuse voters who want to know what happens to their health care if the single-payer bill becomes ...
Will Medicare be moved to private insurance?
That means everyone with comprehensive employee benefits or a private plan through the Affordable Care Act today would be moved onto Medicare.
Who signed onto single payer bills?
With the exception of Harris, Sanders and Rep. Tulsi Gabbard, candidates who signed onto single-payer bills have mostly stopped short of endorsing them on the campaign trail. Instead, they've emphasized proposals that would maintain a role for existing private plans. In O’Rourke's case, he said he had changed his mind.
Does the Sanders bill get rid of supplemental insurance?
Harris said the Sanders bill "doesn't get rid of supplemental insurance," referring to plans that cover other features. She also went on to detail the many benefits voters could expect from their Medicare for All plans, which would include dental and vision.
What is the idea behind Medicare for all?
At the heart of the “Medicare for all” proposals championed by Senator Bernie Sanders and many Democrats is a revolutionary idea: Abolish private health insurance. Proponents want to sweep away our complex, confusing, profit-driven mess of a health care system and start fresh with a single government-run insurer that would cover everyone.
Who is the Democratic candidate for Medicare for All?
Sanders, independent of Vermont, ran on the idea in his 2016 campaign, and now five 2020 Democratic aspirants have co-sponsored one of the two Medicare-for-all bills.
How many people are employed by private health insurance?
The private health insurance business employs at least a half a million people, covers about 250 million Americans, and generates roughly a trillion dollars in revenues. Its companies’ stocks are a staple of the mutual funds that make up millions of Americans’ retirement savings.
Is there a single payer system in Europe?
In Britain, for example, everyone is covered by a public system, but people can pay extra for insurance that gives them access to private doctors. Most countries in Europe don’t have single-payer systems, but instead allow private insurance companies to compete under extremely tight regulations. Image.
Do people buy private insurance?
Even there, people buy private insurance for benefits that are not covered by the government program, like prescription drugs and dental care. Most other countries with single-payer systems allow a more expansive, competing role for private coverage.
Do insurance bills give relief to workers?
While the bills would give relief to insurance industry workers, they would provide no such compensation for investors. Not surprisingly, the insurance industry and many other health care industries vociferously oppose these plans and plan to spend heavily in fighting them.
Is Medicare for All universal health care?
Yes. “Under Medicare for All, everybody in the country would be in this one program,” Friedman says, adding, “The government would be the payer, and everybody would be enrolled.”
What services would Medicare for All cover?
Medicare for All “would provide every single person access to the comprehensive set of health care services in this country,” El-Sayed says. That’s actually much more than Medicare covers today.
Could I keep my private insurance or coverage through my employer?
No. El-Sayed says that the federal government would be “buying you out” of your private insurance under Medicare for All. This single-payer model has been championed by Sanders and Warren.
Could I keep my doctor?
Yes. “If Medicare or a national health insurance program is your insurer, and it is the insurer for everyone, then it basically becomes incumbent on every doctor and hospital to accept it," El-Sayed says. "In fact," he adds, "your access to whatever doctor you choose to see actually expands.”
What would Medicare for All cost?
Nothing. You would not pay anything directly to a health care provider, clinic, hospital or insurer. Tax dollars would pay for all of the services you would receive under Medicare for All. “By eliminating copays and deductibles, people would have access to health care,” Friedman says. “People don’t go to the doctor because they can’t afford it.”
Why does the National Business Group on Health want to preserve employer-sponsored insurance?
Meanwhile, the National Business Group on Health, which represents large employers that mostly self-fund employee health benefits, wants to preserve employer-sponsored insurance because its surveys show workers are satisfied.
How can hospitals become more efficient?
Still, researchers claimed hospitals could become efficient in other ways, such as negotiating better rates for services, negotiating stable staff salaries or forgoing plans to upgrade their facilities.
What does Wichmann say about universal healthcare?
Like UnitedHealth Group, the Partnership for America’s Health Care Future wants to preserve and build on the existing system.
Do hospitals subsidize commercial insurance?
Some studies support those claims. Commercial insurance rates are generally much higher than Medicare and Medicaid rates, which don’t fully cover the cost of caring for a patient. So hospitals say they subsidize people in those programs with the payments they get for commercially insured patients.
Is UnitedHealth a publicly traded company?
The largest publicly traded health insurers in recent years have branched out into other businesses through acquisitions. UnitedHealth Group—the parent of the nation’s largest insurer, UnitedHealthcare—for instance, has amassed an army of employed physicians in its OptumHealth unit.
Who is the CEO of Humana?
Humana CEO Bruce Broussard told an audience at the Barclays Global Healthcare Conference in March that proposals expanding public health coverage represent a “great opportunity” for Humana and the industry to “expand the population that it’s coordinating care with.”.
Can insurance companies survive if their revenue evaporates?
Insurers with a hand in care delivery, analytics or other services could potentially survive even if their insurance revenue evaporated. More incremental approaches to expanding public insurance programs, such as Medicare buy-in or a public option, may have a better chance of gaining support and political traction.