
To receive Medicare benefits, you must first: Be a U.S. citizen or legal resident of at least five (5) continuous years, and Be entitled to receive Social Security benefits.
Full Answer
How many tax credits do I need to qualify for Medicare?
Medicare Starter Kit. Note: Earning 40 credits through payroll taxes while working guarantees that you will not have to pay premiums for Part A benefits (mainly coverage for inpatient hospital care). You do not need any work credits to qualify for Part B (mainly doctors’ services and outpatient care) or for Part D (prescription drug coverage).
Who is eligible for Medicare?
Medicare is our country’s federal health insurance program for people age 65 or older. People younger than age 65 with certain disabilities, or permanent kidney failure, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (Lou Gehrig’s disease), can also qualify for Medicare.
How many people are enrolled in Medicare Part D in 2017?
For 2017, the number of beneficiaries enrolled in Medicare Part D is expected to increase by about 4 percent to 44.5 million, including about 12.7 million beneficiaries who receive the low‑income subsidy.
When can I enroll in Medicare?
8), the first time you’re eligible for Medicare. You can also enroll during the annual Medicare open enrollment period from October 15 – December 7 each year. The effective date for the enrollment is January 1 of the upcoming year.
What are the 3 stages of meaningful use?
Stages of Meaningful Use The meaningful use objectives will evolve in three stages: Stage 1 (2011-2012): Data capture and sharing. Stage 2 (2014): Advanced clinical processes. Stage 3 (2016): Improved outcomes.
What are CMS rules?
CMS regulations establish or modify the way CMS administers its programs. CMS' regulations may impact providers or suppliers of services or the individuals enrolled or entitled to benefits under CMS programs.
What is the meaningful use program?
'Meaningful Use' is the general term for the Center of Medicare and Medicaid's (CMS's) electronic health record (EHR) incentive programs that provide financial benefits to healthcare providers who use appropriate EHR technologies in meaningful ways; ways that benefit patients and providers alike.
What is meaningful use stage2?
Meaningful use stage 2 is the second phase of the meaningful use incentive program that details the second phase of requirements for the use of electronic health record (EHR) systems by hospitals and eligible health care providers.
What is Medicare compliance?
The Medicare Compliance Program is specifically designed to prevent, detect, and correct noncompliance as well as fraud, waste, and abuse.
What is Medicare Final Rule?
The final rule adds Star Ratings (2.5 or lower), bankruptcy or bankruptcy filings, and exceeding a CMS designated threshold for compliance actions as bases for CMS denying a new application or a service area expansion application.
What are the requirements for meaningful use?
To fulfill the requirements for Meaningful Use, eligible professionals must successfully complete the 3 main components of the program: 1) use certified EHR, 2) meet core and menu set objectives, and 3) report clinical quality measures.
Is meaningful use still in effect 2021?
This question comes up a lot. We've got a simple answer: No, it's not – but the name is. The EHR Incentive Program, commonly known as Meaningful Use (MU), has been considered over or has “died” many times, but it is still around.
What is one of the base requirements for meaningful use?
There are three basic components of meaningful use: 1) The use of a certified EHR in a meaningful manner. 2) The electronic exchange of health information to improve quality of health care. 3) The use of certified EHR technology to submit clinical quality and other measures.
What is meaningful use stage1?
Meaningful use stage 1 is the first phase of the United States federal government's meaningful use incentive program, which details the requirements for the use of electronic health record (EHR) systems by hospitals and eligible health care professionals.
What are the 5 main objectives of meaningful use?
MIPS Builds on Meaningful Use Improve quality, safety, efficiency, and reduce health disparities. Engage patients and family. Improve care coordination, and population and public health. Maintain privacy and security of patient health information.
When did Meaningful Use Stage 1 start?
2009-2010. The short history of Meaningful Use begins in 2009 with the enactment of the American Reinvestment and Recovery Act (ARRA) and the accompanying Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act.
How much did Medicare save in 2017?
The FY 2017 Budget includes a package of Medicare legislative proposals that will save a net $419.4 billion over 10 years by supporting delivery system reform to promote high‑quality, efficient care, improving beneficiary access to care, addressing the rising cost of pharmaceuticals, more closely aligning payments with costs of care, and making structural changes that will reduce federal subsidies to high‑income beneficiaries and create incentives for beneficiaries to seek high‑value services. These proposals, combined with tax proposals included in the FY 2017 President’s Budget, would help extend the life of the Medicare Hospital Insurance Trust Fund by over 15 years.
What is the Medicare premium for 2016?
The Bipartisan Budget Act of 2015 included a provision that changed the calculation of the Medicare Part B premium for 2016. Due to the 0 percent cost-of-living adjustment in Social Security benefits, about 70 percent of Medicare beneficiaries are held harmless from increases in their Part B premiums for 2016 and continue to pay the same $104.90 monthly premium as in 2015. The remaining 30 percent of beneficiaries who are not held harmless would have faced a monthly premium this year of more than $150 (a nearly 50 percent increase from 2015). Under the Act, these beneficiaries will instead pay a standard monthly premium of $121.80, which represents the actuary’s premium estimate of the amount that would have applied to all beneficiaries without the hold harmless provision plus an add-on amount of $3. In order to make up the difference in lost revenue from the decrease in premiums, the Act requires a loan of general revenue from Treasury to the Part B Trust Fund. To repay this loan, the standard Part B monthly premium in a given year is increased by the $3 add-on amount until this loan is fully repaid, though the hold harmless provision still applies to this $3 premium increase. This provision will apply again in 2017 if there is a zero percent cost-of-living adjustment from Social Security.
What is the evidence development process for Medicare Part D?
It will be modeled in part after the coverage with evidence development process in Parts A and B of Medicare and based on the collection of data to support the use of high cost pharmaceuticals in the Medicare population. For certain identified drugs, manufacturers will be required to undertake further clinical trials and data collection to support use in the Medicare population, and for any relevant subpopulations identified by CMS. Part D plans will be able to use this evidence to improve their clinical treatment guidelines and negotiations with manufacturers. The proposal helps to ensure that the coverage and use of new high-cost drugs are based on evidence of effectiveness for specific populations. [No budget impact]
What is the MACRA law?
On April 16, 2015, the President signed the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015 (MACRA) into law. The law repealed the Sustainable Growth Rate Formula, established stable payments updates for physicians under Medicare, and promoted value-based payments and participation in alternative payment models. Furthermore, it includes a number of other provisions that affect Medicare, most notably requiring that Social Security numbers be removed from Medicare identification cards. Overall, the Congressional Budget Office estimated that the law will increase Medicare spending by a net $118 billion over 11 years (FY 2015-FY 2025).
What are the priorities of the HHS?
HHS is committed to working with its federal and non-federal partners and stakeholders to improve the market for affordable, innovative drugs and biologics. HHS’s key priorities in this effort are: 1 Increasing Access to Information: Greater visibility into the economics of drug development and pricing provides patients and providers with relevant information to support better health care decisions. 2 Driving Innovation: The Department is working to advance research and promote innovation through expanded efforts in genomics and personalized medicine, including development of new therapeutic approaches and advancement of regulatory models. 3 Strengthening Incentives and Promoting Competition: HHS supports purchasing strategies that address costs, while improving the access and affordability of drugs for beneficiaries. The Department is working to better align financial incentives for providers, drug manufacturers, and other insurers with our goals for better care, smarter spending, and healthier people.
When will hospitals receive bonus payments?
Under this proposal, hospitals that furnish a sufficient proportion of their services through eligible alternative payment entities will receive a bonus payment starting in 2022. Bonuses would be paid through the Inpatient Prospective Payment System permanently and through the Outpatient Prospective Payment System until 2024. Each year, hospitals that qualify for this bonus will receive an upward adjustment to their base payments. Reimbursement through the inpatient and outpatient prospective payment systems to all providers will be reduced by a percentage sufficient to ensure budget neutrality. [No budget impact]
Can Medicare appeals be held without a hearing?
This proposal allows the Office of Medicare Hearings and Appeals to issue decisions without holding a hearing if there is no material fact in dispute. These cases include appeals, for example, in which Medicare does not cover the cost of a particular drug or the Administrative Law Judge cannot find in favor of an appellant due to binding limits on authority. [No budget impact]
What are the new rules for Medicare home health?
On January 9, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) toughened the health and safety standards a home health agency must meet to be a Medicare or Medicaid approved provider.
How does Medicare improve home health?
Good care begins with an efficiently run home health agency fully committed to improvement. As leadership has a major impact on the success of an organization, Medicare is increasing the qualifications for home health administrators and clinical managers. In terms of administration, the new standards also call for a simplified organizational structure. Although chain of command will likely be simplified with the new standards, such hierarchy won’t be eliminated entirely. The common structure of a parent agency that oversees branches will be retained. This kind of structure allows the overall business model to grow while catering to the needs of local markets. In turn, it helps consumers by making sure that Medicare as an agency understands individual needs, especially when it comes to home healthcare.#N#The CMS also wants to improve customer satisfaction by requiring individual agencies to implement ongoing evaluation to enhance patient care. Although quality assessment and performance improvement (QAPI) may be a new term to much of the general public, its basic premise is not. Home health agencies are expected to collect objective data on their own performance, reflect upon it and use it as the basis for improving patient care. CMS has, in fact, used QAPI to devise many of its new standards.
What is CMS home healthcare?
The new CMS standards for home healthcare agencies are based on established research and standards of practice common to hospitals, clinics and other healthcare facilities. Streamlining agency structure will improve patient outcome, as will raising accountability and offering guidelines for best practices across the industry. The end result should be better patient care, more satisfied Medicare beneficiaries and more responsible use of the program’s resources.
What is the CMS system of communication?
To that end, CMS has instituted an integrated communication system that requires healthcare workers across disciplines to continually identify and respond to patient needs. Timely and detailed interaction among all professionals involved in home care that will lead to faster, more focused intervention.#N#Patients are also expected to directly benefit from this set of standards, as a key component of the new standards is providing each home care patient and their caregivers with written direction regarding:
How long do you have to live to qualify for Medicare?
You qualify for full Medicare benefits if: You are a U.S. citizen or a permanent legal resident who has lived in the United States for at least five years and. You are receiving Social Security or railroad retirement benefits or have worked long enough to be eligible for those benefits but are not yet collecting them.
How old do you have to be to get Medicare?
citizen or have been a legal resident for at least five years, you can get full Medicare benefits at age 65 or older. You just have to buy into them by: Paying premiums for Part A, the hospital insurance.
How much will Medicare premiums be in 2021?
If you have 30 to 39 credits, you pay less — $259 a month in 2021. If you continue working until you gain 40 credits, you will no longer pay these premiums. Paying the same monthly premiums for Part B, which covers doctor visits and other outpatient services, as other enrollees pay.
How many credits do you get in 2021?
Work credits are earned based on your income; the amount of income it takes to earn a credit changes each year. In 2021 you earn one work credit for every $1,470 in earnings, up to a maximum of four credits per year. If you have accrued fewer than 30 work credits, you pay the maximum premium — $471 in 2021.
How long do you have to be on disability to receive Social Security?
You have been entitled to Social Security disability benefits for at least 24 months (that need not be consecutive); or. You receive a disability pension from the Railroad Retirement Board and meet certain conditions; or.
How long do you have to be a US citizen to qualify for Medicare?
To receive Medicare benefits, you must first: Be a U.S. citizen or legal resident of at least five (5) continuous years, and. Be entitled to receive Social Security benefits.
How long does it take to enroll in Medicare?
If you don’t get automatic enrollment (discussed below), then you must sign up for Medicare yourself, and you have seven full months to enroll.
How old do you have to be to get a Medigap policy?
In other words, you must be 65 and enrolled in Medicare to sign up for a Medigap policy. Once you’re 65 and enrolled in Part B, you have six months to enroll in Medigap without being subject to medical underwriting. During this initial eligibility window, you can: Buy any Medigap policy regardless of health history.
How long do you have to sign up for Medicare before you turn 65?
And coverage will start…. Don’t have a disability and won’t be receiving Social Security or Railroad Retirement Board benefits for at least four months before you turn 65. Must sign up for Medicare benefits during your 7-month IEP.
When do you sign up for Medicare if you turn 65?
You turn 65 in June, but you choose not to sign up for Medicare during your IEP (which would run from March to September). In October, you decide that you would like Medicare coverage after all. Unfortunately, the next general enrollment period doesn’t start until January. You sign up for Parts A and B in January.
When does Medicare open enrollment start?
You can also switch to Medicare Advantage (from original) or join a Part D drug plan during the Medicare annual open enrollment period, which runs from October 15 through December 7 each year. Eligibility for Medicare Advantage depends on enrollment in original Medicare.
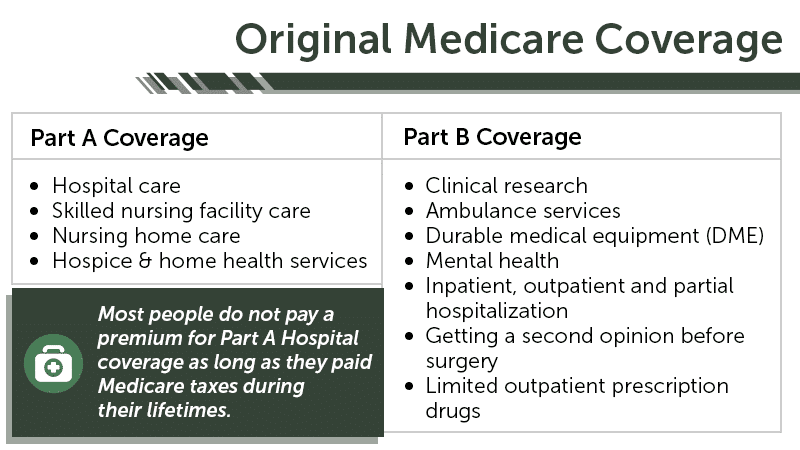
How many parts are there in Medicare?
There are four parts to the program (A, B, C and D); Part C is a private portion known as Medicare Advantage, and Part D is drug coverage. Please note that throughout this article, we use Medicare as shorthand to refer to Parts A and B specifically.
What is the increase in Medicare operating rates for FY 2017?
4. Under the FY 2017 final rule, acute care hospitals that report quality data and that are meaningful users of EHRs will receive a 0.95 percent increase in Medicare operating rates. 5.
What is Medicare's role in the reform movement?
Medicare has played a prominent part in various reform movements, including the shift from fee-for-service to value-based payment models, and the program's policies and reimbursement rates have acted as a catalyst for change nationwide.
How much will Medicare disproportionate share hospital payments be reduced by?
As part of the ACA, Medicare disproportionate share hospital payments will be reduced by 75 percent, or $49.9 billion, by 2019. CMS said in the FY 2017 final IPPS rule it will distribute nearly $6 billion in DSH payments in FY 2017, about $400 million less than in FY 2016. 10.
How much was the Home Health Perspective Payment System reduced in 2017?
32. Under the final rule, CMS estimates Medicare payments to home health agencies will be reduced by 0.7 percent, or $130 million, in 2017. 33.
What language do you need to translate Medicare?
Medicare Part C plans and Part D sponsors (sponsors) are required to translate the materials described below into any non-English language that is the primary language of at least 5 percent of the individuals in a plan benefit package (PBP) service area.1 Pursuant to the Medicare Marketing Guidelines (MMG), sponsors that have service areas that meet the 5% threshold must provide specific translated materials on their websites and in hard-copy upon beneficiary request.2 Translation requirements for Medicare Medicaid Plans (MMPs) are detailed in the three-way contracts as well as in each State-specific marketing guidance document on the CMS website.3
Does CMS translate Part C and D?
CMS has translated several of the Part C and D contract year (CY) 2017 model materials to alleviate some of the translation burden on sponsors and provide consistency among translated materials. The specific Part C and D materials CMS translated are listed in Table 1. Sponsors must update the CMS-provided translations consistent with the May 10, 2016 HPMS memo entitled Contract Year 2017 Annual Notice of Change/Evidence of Coverage Submission Requirements and Yearly Assessment. Sponsors are free to continue to develop their own translations and, as needed, adapt the translations to accommodate the particular language needs of their members (e.g., Spanish speaking beneficiaries in Puerto Rico may be familiar with certain translations of health care terminology that may differ from how those terms are typically translated for Spanish speakers in the United States). Please be aware that we did not translate all model materials that must be translated.
