Key Takeaways
- Medicare is the primary medical coverage provider for seniors and those with a disability.
- Medicaid is designed for people with limited income.
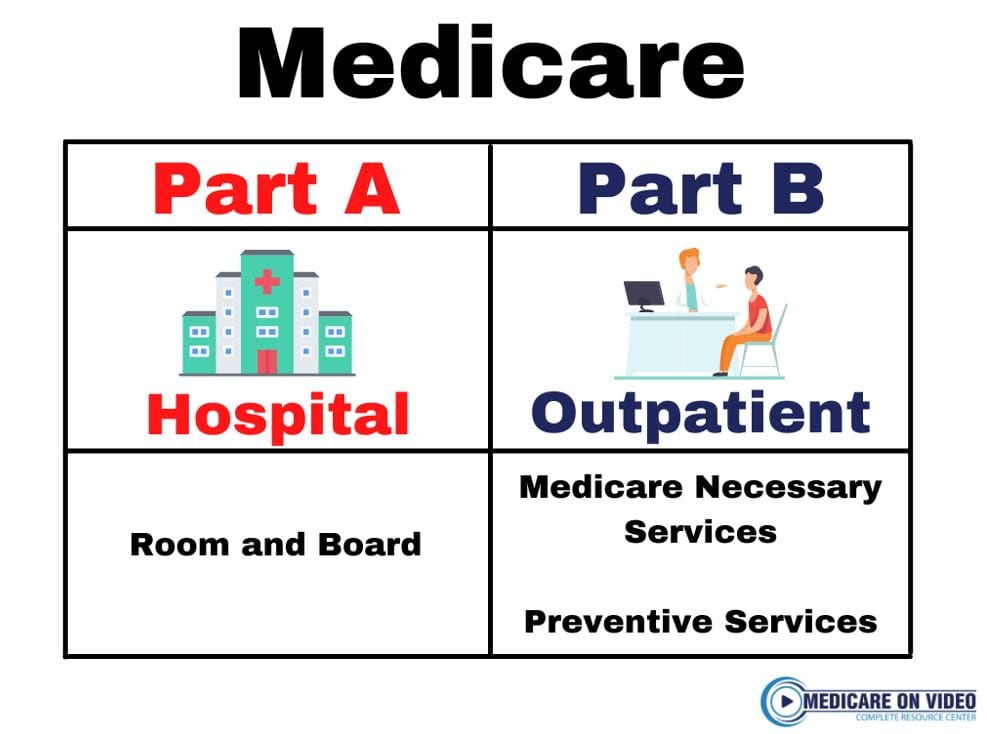
- Medicare has four parts that each cover different things—hospitalization, medically necessary services, supplemental coverage, and prescription drugs.
How does Medicare compare to Medicaid?
Mar 10, 2022 · Broadly speaking, Medicare covers seniors and people with disabilities. Medicaid assists people with low income. Yet Medicare and Medicaid services do overlap sometimes. Medicare helps people with low income through a financial aid program called Extra Help.
Which is better Medicare or Medicaid?
Mar 17, 2022 · Key Takeaways. Medicare is mostly based on age, while Medicaid is a welfare program based on income. Its purpose is to help people with low incomes without regard to age. Medicare Parts A and B do not include dental care, but Medicaid may cover some dental care and treatment for adults in some states.
Is Medicaid and Medicare the same thing?
Apr 13, 2022 · Medicare A federal health insurance program that provides coverage to people 65 and older and to those under 65 who have a disability, regardless of income. Medicaid A state and federal assistance program that provides health coverage to people who have very low incomes. Dual Eligibility
What is the difference between Medicare and Medicaid?
This often comes in the form of Medicaid. Medicaid is a program provided by the federal government for those who qualify due to disability or low income. It covers some or all of the costs of Medicare. Medicaid can help cover services that Medicare doesn’t cover, or only partially covers, such as: Nursing home care; Personal care

What are the key differences between Medicare and Medicaid?
Medicare is a federal program that provides health coverage if you are 65+ or under 65 and have a disability, no matter your income. Medicaid is a state and federal program that provides health coverage if you have a very low income.
What are the disadvantages of Medicaid?
Disadvantages of MedicaidLower reimbursements and reduced revenue. Every medical practice needs to make a profit to stay in business, but medical practices that have a large Medicaid patient base tend to be less profitable. ... Administrative overhead. ... Extensive patient base. ... Medicaid can help get new practices established.
Is it good to be on Medicaid?
Conclusion. Medicaid provides comprehensive coverage and financial protection for millions of Americans, most of whom are in working families. Despite their low income, Medicaid enrollees experience rates of access to care comparable to those among people with private coverage.Mar 6, 2019
What does Medicaid cover for seniors?
Medicaid and Medicare: The Basics If a loved one qualifies financially for Medicaid and meets the functional eligibility requirements, then Medicaid will help pay for long-term care services like nursing home care, and home and community-based services like home health care.
What is the difference between Medicare and Medicaid?
A key difference between Medicare and Medicaid is that one is primarily age-based, and the other is an income-based welfare program benefiting people with limited financial resources, regardless of age. Medicare is available to assist people 65 or older, and in some cases people under 65 with specific medical disabilities or diseases.
When did Medicare and Medicaid become part of the government?
In 1965, an amendment to the Social Security Act established Medicare and Medicaid, two government-run health programs. Their similar names can often lead to confusion about what each program covers. In some cases, people may be eligible to be covered by both programs.
How many people will be covered by medicaid in 2021?
According to The Kaiser Family Foundation, more than 80 million individuals, were covered by Medicaid/CHIP in the United States in as of January 2021. 1. Medicaid federal rules specify certain mandatory benefits and each state may choose to offer optional benefits in addition to the basics.
How old do you have to be to qualify for Medicare?
How to Qualify for Medicare: Eligibility for Parts A, B, and C. Medicare Part A Eligibility: In most cases, you must be 65 years or older. You may qualify for Medicare if you are under 65 with certain disabilities or conditions, end-stage renal disease, or Lou Gehrig's disease.
Does Medicare cover dental care?
Medicare parts A and B do not include dental care like cleanings, fillings, tooth extractions, dentures, dental plates, or other dental devices, whereas Medicaid may cover preventative dental care for adults in some states, as well as treatment in others. This varies by state but can be a definite advantage over Medicare alone.
Is Medicare federally managed?
Also, Medicaid coverage and eligibility varies from state to state due to the fact that it is both federally and state managed. Medicare basics are standardly Federally managed.
Is Medicare confusing?
Trying to understand all the information about Medicare or Medicaid can be very confusing. There are many programs available and making the right choice is often hard. There are thankfully many places to get free information to help you make good decisions. There are also additional programs that may be available depending on what needs you have.
What Is Medicare?
Medicare is a federal health insurance program offered to U.S. citizens who are 65 and older. Younger people with disabilities, as well as as well as some younger people with disabilities who are on Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) (although eligibility typically happens after a 2 year waiting period following enrollment in SSDI).
Medicare Parts
Medicare comes broken into parts: Part A, B, C, and D. Each part covers different things, and comes with different enrollment procedures and costs. Here’s a basic breakdown:
What Is Medicaid?
If you find yourself struggling to afford the cost of your healthcare, you may qualify for federal and state subsidies. This often comes in the form of Medicaid. Medicaid is a program provided by the federal government for those who qualify due to disability or low income. It covers some or all of the costs of Medicare.
How Do I Know If I Qualify?
According to medicare.gov, you may be eligible for Medicaid if you have limited income and are:
What Does Medicaid Cover?
When you enroll in Medicaid, you may be able to get access to health care benefits such as:
Can I Have Both Medicare and Medicaid?
It’s possible to qualify for both Medicare and Medicaid. If you qualify for both Medicare and Medicaid, it’s referred to as having “Dual Eligibility”. People who have both Medicare and full Medicaid will likely have all of their healthcare costs covered.
What is Medicare Advantage?
Medicare Advantage, or Part C, is a newer health insurance policy that groups together all the parts of Original Medicare. It will typically cover the deductibles, out-of-pocket maximums and premiums for Original Medicare Part A and B and will provide additional coverage benefits such as dental, hearing and prescription drugs.
What is the income level for medicaid?
In order to be eligible for Medicaid coverage, you would need to have an income level below 133% of the Federal Poverty Level (or 138% in Medicaid in expanded states), be pregnant or have a disability.
What is the difference between Medicare Part B and Part D?
Part B provides coverage for doctors, medical tests and some procedures, while Part D is designed to offset the costs of prescription drugs. By enrolling in Medicare Part B and D, an individual can get closer to having a comprehensive health insurance policy.
What is the health insurance policy for 2021?
In the United States, there are currently two government-provided health insurance policies that citizens can enroll in: Medicare and Medicaid. While they both provide general health insurance benefits, there are differences in eligibility and coverage that are crucial to identify and be aware ...
What is a QDWI?
Qualified Disabled Working Individual (QDWI) Program. All of these programs would provide extra help for covering premiums, deductibles and coinsurance for Medicare. If you don't qualify for Medicaid when you are enrolled in Medicare, there are still options to help provide financial aid for Part A, B and D deductibles.
Is Medicare based on income?
It is key to note that eligibility for Medicare is not based upon your income. For most U.S. citizens, during their working years, they would have paid a tax into the Social Security fund. By paying into this pool of tax dollars, you would be automatically enrolled in the Medicare plan when you turn 65 years of age.
Medicare Explained
Medicare is an exclusively federal program enacted by law in 1965 and designed to provide fee-for-service health coverage for seniors and other qualifying individuals. Because Medicare is a federal program, benefits are generally the same from state to state.
Medicaid Explained
Medicaid is a federal health coverage program for children and certain qualifying adults. It’s administered by states and funded jointly by the federal government and individual states through fund-matching. It was signed into law at the same time as Medicare in 1965.
Medicare vs. Medicaid Coverage of Senior Care
Both Medicare and Medicaid cover some expenses associated with assisted living, but those costs are limited and very specific. Below, we break down what both Medicare and Medicaid do and do not cover when it comes to long-term senior care.
How does Medicare vs Medicaid work?
Medicare vs Medicaid: How Medicaid Works. Medicaid is a need-based joint federal and state insurance program that covers low-income individuals and families. That said, Medicaid coverage can vary significantly from state to state. That’s because the federal government covers up to 50% of each state’s Medicaid program costs.
How much does the federal government cover for medicaid?
That’s because the federal government covers up to 50% of each state’s Medicaid program costs. This means all remaining Medicaid program costs must be paid for at the state level. Unlike Medicare, Medicaid isn’t available to everyone and it has very strict eligibility requirements.
How long does it take to get medicaid if you have SSDI?
But if your disability started long before you applied for SSDI, that time counts toward your mandatory two-year waiting period. In addition, individuals with very low income and assets may qualify for Medicaid during the two-year Medicare waiting period.
How does Medicare work?
Medicare provides coverage for Americans who: Here’s how Medicare payments work: Essentially, your Social Security taxes go into a trust fund that grows throughout your working years. Money from that trust fund then pays all eligible bills incurred by people covered under the Medicare program.
How long does it take to get a disability after you have Lou Gehrig's disease?
While that two-year waiting period sounds like a long time, it’s calculated using your original SSDI entitlement date. For most people, that means five months after the date when your disability began.
What is Medicare Part B?
Medical: Medicare Part B works like most private insurance policies and covers doctor’s visits, lab work, and visits to the emergency room. Prescription Drugs: Medicare Part D helps cover prescribed medication costs. Medicare Part A and B participants are eligible for Part D (or you can purchase it as a standalone plan).
When did Medicare expand to cover disabled people?
When Congress expanded Medicare to cover seriously disabled Americans in 1972, the law also mandated that SSDI two-year waiting period. For this reason, the Social Security Administration (SSA) isn’t likely to change that requirement anytime soon.
