Social Security will be the biggest expense, budgeted at $1.196 trillion. It's followed by Medicare at $766 billion and Medicaid Medicaid in the United States is a federal and state program that helps with medical costs for some people with limited income and resources. Medicaid also offers benefits not normally covered by Medicare, including nursing home care and personal care services. The Health Insurance As…Medicaid
Full Answer
What percentage of the federal budget goes to Medicaid?
Medicare spending often plays a major role in federal health policy and budget discussions, since it accounts for 21% of national health care spending and 12% of the federal budget. 18 How Does Medicaid Expansion Affect State Budgets?
How is Medicare and Medicaid funded?
Medicaid is funded by the federal government and each state. Both programs received additional funding as part of the fiscal relief package in response to the 2020 economic crisis. Medicare is administered by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), a component of the Department of Health and Human Services.
What costs are covered by Medicare?
Both Medicare Part A and Part B copays and coinsurance. The Medicare Part D premium, deductibles and copays for prescription drugs. Coverage for those costs is available through the Extra Help program, which Medicaid and Medicare Savings Program enrollees automatically qualify for.
Who decides how much Social Security benefits we pay each year?
While Congress does not set the amount of benefits we pay each year, they decide funding for our administrative budget. Our administrative budget provides resources to administer Social Security and SSI programs as well as certain aspects of the Medicare program.
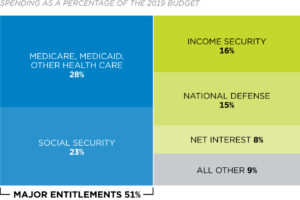
How much of the federal budget does Medicare and Social Security absorb?
Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid already absorb 42 percent of the federal budget and are growing by 7 percent annually, making them the largest impediment to balancing the budget. Furthermore, many believe that anyone over age 55 should be exempt from entitlement reforms.
How is Medicare Part A funded?
Medicare Part A is funded by payroll taxes that are theoretically "saved" in a trust fund for future retirees. Parts B and D are not funded by payroll taxes. As with Social Security, Congress has already spent all past surpluses for Part A, leaving taxpayers to fund all future shortfalls from scratch.
What is Medicare Part A?
Medicare. Medicare was created in 1965 to provide medical care to Americans age 65 and older. An average of just under $10,000 is spent annually on each of Medicare's 43 million enrollees. [18] Medicare has three main components: 1 Medicare Part A covers hospital and skilled nursing care. It is funded by a 2.7 percent payroll tax (split equally between employer and employee) on all income. For most enrollees, Medicare operates as a fee-for-service system, meaning that once the enrollee satisfies a modest deductible, Washington reimburses participating health care providers for services based on a set payment schedule. 2 Medicare Part B covers physical and outpatient care. This optional program, in which most Medicare recipients participate, requires recipients to pay a monthly premium set at approximately 25 percent of total program costs, leaving the taxpayers to fund the remaining 75 percent. 3 Medicare Part D is the new prescription drug benefit enacted in 2003. This optional program is funded mostly from general tax revenues, although enrollees pay a small deductible and monthly premium. Enrollees choose from competing private health plans, which are reimbursed by Washington.
What is the ratio of Social Security to Medicare in 2030?
In 1960, five workers supported each retiree. This ratio has fallen to 3:1 and will drop to 2:1 by 2030. A 2:1 ratio means that each married couple in 2030 will be supporting the Social Security and Medicare benefits of one retiree. Higher benefit levels will drive the rest of the cost increase.
Why is Medicare reform so difficult?
While Social Security transfers income from one group to another and therefore can be fixed with formula changes, fixing Medicare is more difficult because it is a major part of the health care economy.
What will the federal budget be in 2050?
The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) projects that federal spending on Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid will leap from 8.4 percent of GDP today to 18.6 percent by 2050. [2] (See Chart 1.) For comparison, the entire federal budget is 20 percent of GDP (18 percent spent on programs and 2 percent on net interest). This massive cost increase will be fueled by the 77 million retiring baby boomers, combined with steep inflation in health care costs and automatic scheduled benefit hikes.
What is the most misunderstood aspect of Social Security?
The Social Security Trust Fund is the most misunderstood aspect of this program. In 1983, with Social Security's finances in dire straits and baby boomers approaching retirement, lawmakers raised the payroll tax so that Social Security could build a $5 trillion "surplus.".
Why is Medicare underfunded?
Medicare is already underfunded because taxes withheld for the program don't pay for all benefits. Congress must use tax dollars to pay for a portion of it. Medicaid is 100% funded by the general fund, also known as "America's Checkbook.".
How much is Biden's budget for 2022?
President Biden’s budget for FY 2022 totals $6.011 trillion, eclipsing all other previous budgets. Mandatory expenditures, such as Social Security, Medicare, and the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program account for about 65% of the budget. For FY 2022, budget expenditures exceed federal revenues by $1.873 trillion.
What is the budget for 2022?
The discretionary budget for 2022 is $1.688 trillion. 1 Much of it goes toward military spending, including Homeland Security, the Department of Veterans Affairs, and other defense-related departments. The rest must pay for all other domestic programs.
How much is discretionary spending?
Discretionary spending, which pays for everything else, will be $1.688 trillion. The U.S. Congress appropriates this amount each year, using the president's budget as a starting point. Interest on the U.S. debt is estimated to be $305 billion.
What is the most expensive program in 2022?
It also includes welfare programs such as Medicaid. Social Security will be the biggest expense, budgeted at $1.196 trillion.
How long does it take for the President to respond to the budget?
The president submits it to Congress on or before the first Monday in February. Congress responds with spending appropriation bills that go to the president by June 30. The president has 10 days to reply.
Is Social Security covered by payroll taxes?
Social Security costs are currently 100% covered by payroll taxes and interest on investments. Until 2010, there was more coming into the Social Security Trust Fund than being paid out. Thanks to its investments, the Trust Fund is still running a surplus. Important.
Why are Social Security benefits part of the federal government?
The benefits these programs pay are part of the Federal Government’s mandatory spending because authorizing legislation ( Social Security Act) requires us to pay them. While Congress does not set the amount of benefits we pay each year, they decide funding for our administrative budget.
What is the purpose of the Justification of Estimates for Appropriations Committees?
The Justification of Estimates for Appropriations Committees informs members of Congress about SSA’s funding request, including how it will support performance goals and initiatives to improve service. For specific sections, please see the following:
How is Social Security funded?
Social Security is funded through payroll taxes.
How much of Medicare will be paid by 2034?
That means Medicare contributes to the budget deficit. Rising health care costs mean that general revenues would have to pay for 49% of Medicare costs by 2034. 13 As with Social Security, the tax base is insufficient to pay for this.
What is Medicare Part A?
Medicare has two sections: The Medicare Part A Hospital Insurance program, which collects enough payroll taxes to pay current benefits. Medicare Part B, the Supplementary Medical Insurance Program, and Part D, the new drug benefit. Payroll taxes and premiums cover only 57% of benefits.
What does it mean when the government has a high level of mandatory spending?
In the long run, the high level of mandatory spending means rigid and unresponsive fiscal policy. This is a long-term drag on economic growth.
What is mandatory program?
Congress established mandatory programs under so-called authorization laws. 3 These laws also mandated that Congress appropriate whatever funds are needed to keep the programs running. The mandatory portion of the U.S. budget estimates how much it will cost to fulfill these authorization laws.
How much is mandatory spending in 2021?
Mandatory spending is estimated to be $2.966 trillion for FY 2021. 1 The two largest mandatory programs are Social Security and Medicare. That's 38.5% of all federal spending. It's more than two times more than the military budget. 2.
How much is Social Security in 2021?
Social Security is the single largest federal budget item, costing $1.151 trillion in FY 2021. 1 The Social Security Act of 1935 guaranteed that workers would receive benefits after they retired. It was funded by payroll taxes that went into a trust fund used to pay out the benefits. 7
Why do we bundle Medicare payments?
Bundle Medicare’s payments for post-acute care in order to increase incentives for efficiency and cost reduction. Beginning 2018 Medicare beneficiaries would have a choice of remaining in FFS Medicare or going to a Medicare Exchange, where they could choose among competing private health plans.
When will Social Security index the benefit formula?
Beginning in 2023, index the benefit formula for increases in life expectancy , without changing either the age of full retirement or the early retirement age from those in current law and require the Social Security Administration to ensure that early retirees understand that they are opting for a lower monthly benefit.
What is the right thing to do for future Social Security beneficiaries?
But current and future workers need to know that Social Security will be there for them, and the best way to reassure them is to act now to adjust future benefits and revenues. Taking immediate action is the right thing to do for future Social Security beneficiaries.
Why is federal spending on health care and loss of revenue through the exclusion so large?
Federal spending on health care and loss of revenue through the exclusion is so large that addressing it is critical to success of efforts to reduce the deficit enough to control federal debt. Large federal deficit reductions in health will require policies that slow the rate of growth of spending overall.
Is Social Security a deficit reduction plan?
Those who argue that Social Security should not be part of a deficit reduction plan, sometimes point out that Social Security has been running surpluses for decades. Those surpluses were invested in Treasury bonds, which meant the government was borrowing from Social Security to fund other spending.
Is Medicaid funded by the federal government?
Medicaid, the program that provides health coverage to millions of low-income Americans, poses a different set of challenges because it is jointly funded by the federal and state government s, but administered by each state.
How much is Medicare Part A deductible?
The Medicare Part A (hospital insurance) deductible, which for 2019 will be $1,364 for hospital stays. Both Medicare Part A and Part B copays and coinsurance. The Medicare Part D premium, deductibles and copays for prescription drugs. Coverage for those costs is available through the Extra Help program, which Medicaid and Medicare Savings Program ...
Who can answer Medicaid questions?
SHIP counselors can answer some of your Medicaid questions and refer you to local Medicaid officials to help with others. The National Council on Aging has a benefits checkup website that has information on Medicare, Medicaid and other programs that help older Americans.
What is a SLMB?
The Specified Low-Income Medicare Beneficiary (SLMB) program helps pay only for Part B premiums, not the Part A premium or other cost sharing. If your income is too high to qualify for the QMB program, you might qualify for this one. You also automatically qualify for Extra Help for prescription drugs.
What is QDWI in Medicare?
The Qualified Disabled and Working Individuals (QDWI) program only helps pay for Medicare Part A (hospital insurance) premiums. This program is designed for individuals with disabilities, under age 65, who are currently working and lost their premium-free Part A benefit when they began to work.
What is excluded from the $2,000 asset test?
Excluded from the $2,000 asset test are such things as your home, one car, some burial expenses, some life insurance and household and personal items. States generally look back at an applicant’s assets for five years to make sure they haven’t divested themselves of those resources just to qualify for Medicaid.
Does Medicaid cover nursing home care?
Nursing home care and home- and community-based long-term services and supports. In some states, Medicaid will cover benefits that Medicare does not , such as dental care, transportation to and from doctor visits, eyeglasses, physical therapy and other services.
Does full medicaid have higher thresholds?
As with full Medicaid, some states have higher resource thresholds. Casey Schwarz at the Medicare Rights Center says that “one of the biggest problems we see is that people assume they aren’t eligible and don’t apply. People should look into what the income and asset guidelines are for their state.”.
What is the tax rate for Social Security?
The current tax rate for social security is 6.2% for the employer and 6.2% for the employee, or 12.4% total. The current rate for Medicare is 1.45% for the employer and 1.45% for the employee, or 2.9% total. Refer to Publication 15, (Circular E), Employer's Tax Guide for more information; or Publication 51, (Circular A), Agricultural Employer’s Tax Guide for agricultural employers. Refer to Notice 2020-65 PDF and Notice 2021-11 PDF for information allowing employers to defer withholding and payment of the employee's share of Social Security taxes of certain employees.
What is the wage base limit for 2021?
The wage base limit is the maximum wage that's subject to the tax for that year. For earnings in 2021, this base is $142,800. Refer to "What's New" in Publication 15 for the current wage limit for social security wages; or Publication 51 for agricultural employers. There's no wage base limit for Medicare tax.
Introduction
The impact of the Social Security program on the Federal budget has been the subject of much controversy and confusion. Indeed, disagreement between the Social Security and Medicare actuaries resulted in a lengthy addition to the “Statement of Actuarial Opinion” beginning in 2014 and continuing through last year’s Social Security Trustees’ report.
A Budget Perspective
The purpose of the annual Social Security Trustees’ report is to assess the actuarial status of the Old-Age, Survivors and Disability Insurance (OASDI) trust funds.
Conclusion
The Social Security Act identifies certain types of information that “shall” be included in the Trustees’ report but does not define this information, nor does it prohibit the inclusion of other information.