How much of the federal budget goes to Social Security and Medicare?
Social Security alone comprises more than a third of mandatory spending and around 23 percent of the total federal budget. Medicare makes up an additional 23 percent of mandatory spending and 15 percent of the total federal budget. This chart shows where the projected $2.45 trillion in mandatory spending will go in fiscal year 2015.
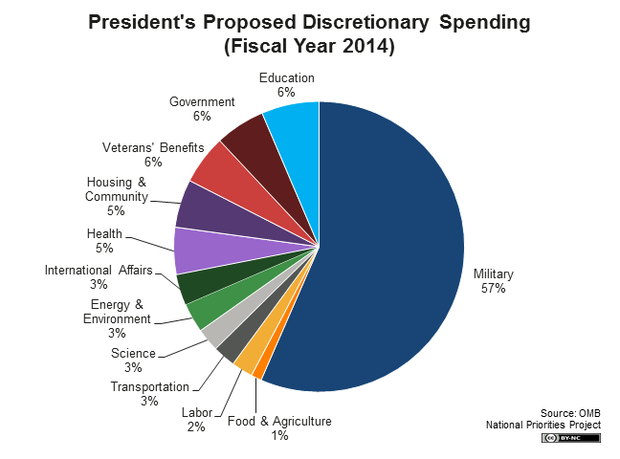
How much of the federal budget goes toward the military?
About $1.485 trillion in FY 2021 goes toward discretionary spending, which pays for all federal government agencies. The largest is the military. 7 The mandatory budget will cost $2.966 trillion in FY 2021. 1 Mandatory spending is skyrocketing, because more baby boomers are reaching retirement age.
How much does the US government spend on government programs?
Government spending for FY 2021 budget is $4.829 trillion. Despite sequestration to curb government spending, deficit spending has increased with the government’s effort to continually boost economic growth. Two-thirds of federal expenses must go to mandatory programs such as Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid.
What percentage of federal budget is mandatory spending?
Mandatory spending makes up nearly two-thirds of the total federal budget. Social Security alone comprises more than a third of mandatory spending and around 23 percent of the total federal budget. Medicare makes up an additional 23 percent of mandatory spending and 15 percent of the total federal budget.

What percent of government spending is military?
Defense spending accounts for more than 10 percent of all federal spending and nearly half of discretionary spending. Total discretionary spending — for both defense and nondefense purposes — is typically only about one-third of the annual federal budget.
What percentage of government spending is Social Security?
Social Security: In 2019, 23 percent of the budget, or $1 trillion, paid for Social Security, which provided monthly retirement benefits averaging $1,503 to 45 million retired workers in December 2019.
What are the 3 largest categories of federal government spending?
The U.S. Treasury divides all federal spending into three groups: mandatory spending, discretionary spending and interest on debt. Together, mandatory and discretionary spending account for more than ninety percent of all federal spending, and pay for all of the government services and programs on which we rely.
What percentage of the federal budget is social programs?
In 2019, major entitlement programs—Social Security, Medicare, Medicaid, Obamacare, and other health care programs—consumed 51 percent of all federal spending, larger than the portion of spending for other national priorities (such as national defense) combined.
What percentage of federal taxes go to military?
In short, roughly 20 percent of the federal budget is dedicated to defense and security, which can be understood as the percent of tax dollars spent on the military. But if you are interested in this topic, make sure you read until the very end of the article to find out everything there is to know!
What is the biggest part of the US budget?
Social Security takes up the largest portion of the mandatory spending dollars. In fact, Social Security demands $1.046 trillion of the total $2.739-trillion mandatory spending budget. It also includes programs like unemployment benefits and welfare.
Where does the majority of taxes go?
As you might have expected, the majority of your Federal income tax dollars go to Social Security, health programs, defense and interest on the national debt.
What is the largest source of income for the federal government?
individual income taxesThis is especially important as the economic recovery from the pandemic continues. In the United States, individual income taxes (federal, state, and local) were the primary source of tax revenue in 2020, at 41.1 percent of total tax revenue.
What are the top 5 things the government spends money on?
Military (Discretionary)Social Security, Unemployment, and Labor (Mandatory)Medicare and Health (Mandatory)Government (Discretionary)Education (Discretionary) Whether you owe money to the IRS or you have a State tax debt, our staff of Enrolled Agents and Tax Professionals can help you!
What percentage of the federal budget goes toward Medicare?
Medicare accounts for a significant portion of federal spending. In fiscal year 2020, the Medicare program cost $776 billion — about 12 percent of total federal government spending. Medicare was the second largest program in the federal budget last year, after Social Security.
What is the next largest expense for Social Security?
10 It also means that Congress can no longer "borrow" from the Social Security Trust Fund to pay for other federal programs. Medicare ( $722 billion) and Medicaid ($448 billion) are the next largest expenses.
How much will Medicaid cost in 2030?
By 2030, the cost will almost double to $665 billion, exceeding that of Medicaid. 1 It's not a mandatory program, but it must be paid in order to avoid a U.S. debt default. These estimates will increase if interest rates rise.
How much is the national debt in 2021?
These are part of mandatory spending, which are programs established by prior Acts of Congress. The interest payments on the national debt total $378 billion for FY 2021. They are necessary to maintain faith in the U.S. government. About $1.485 trillion in FY 2021 goes toward discretionary spending, which pays for all federal government agencies.
What is the budget for FY 2021?
Key Takeaways. Government spending for FY 2021 budget is $4.829 trillion. Despite sequestration to curb government spending, deficit spending has increased with the government’s effort to continually boost economic growth. Two-thirds of federal expenses must go to mandatory programs such as Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid.
How much will the mandatory budget cost in 2021?
The mandatory budget will cost $2.966 trillion in FY 2021. 1 Mandatory spending is skyrocketing, because more baby boomers are reaching retirement age. By 2030, one in five Americans will be older than 65. 8
How much is discretionary spending?
Discretionary spending is $1.485 trillion. 1 It pays for everything else. Congress decides how much to appropriate for these programs each year. It's the only government spending that Congress can cut. 12
How much is the emergency fund for FY 2021?
For FY 2021, the emergency fund is $74.3 billion. The largest component is Overseas Contingency Operations (OCO) that pay for wars. 13 . Once you include the OCO fund, then security-related spending is $915.1 billion. It's spread out among different agencies and budget categories, so you must add it all together.
What is the additional type of spending that impacts federal spending?
An additional type of spending that impacts federal spending is. supplemental appropriations. , also referred to as supplemental spending. In 2020, the U.S. Congress passed four supplemental. appropriations.
Where does Medicare and Social Security money come from?
The majority of Social Security and Medicare funding comes from tax revenue and interest on trust fund reserves. For 2019, income for these programs was $1.86 trillion. However, costs exceeded revenue starting in 2018 for Medicare Part A and are expected to exceed revenue beginning in 2021 for Social Security.
Why is Social Security mandatory?
Programs like Social Security, Medicare, and various income security programs, are based on laws previously established that dictate the money budgeted for spending each year, which is why spending for those programs is referred to as mandatory.
How much does Social Security cost?
In 2019, the cost of the Social Security and Medicare programs was $1.86 trillion.
What does the government buy?
The government buys a variety of products and services used to serve the public — everything from military aircraft, construction and highway maintenance equipment, buildings, and livestock, to research, education, and training.
When will Medicare be depleted?
While Medicare Parts B and D are largely funded by general revenues and beneficiary premiums, the Boards project that Medicare Part A trust fund will be depleted by 2026 and the Social Security trust fund will be depleted by 2034.
What are the three types of federal spending?
There are three types of federal spending: mandatory, discretionary, and interest on debt. Discretionary spending is set by Congress after an analysis of annual appropriations. In FY 2015, 29 percent of all federal funds were discretionary, and 54 percent of these (more than half) went to the military. To further emphasize just how much money is ...
How much is the military budget for 2017?
It comes from the discretionary federal budget and will equal about $773.5 billion for Fiscal Year 2017. The budget is divided up between different operations and departments within the DOD and between the various military branches. There are three types of federal spending: mandatory, discretionary, and interest on debt.
What is the most expensive military in the world?
The U.S. Military Budget Compared to Other Nations. America’s military is not just the most powerful in the world; it’s also the most expensive. By far, the United States spends more money on it’s military than any other country in the world.
Should the DoD reduce spending on personnel?
In their efforts to save money, the DoD could and should reduce spending in personnel and maintenance, such as the number of civilians it employs, the amount of benefits per soldier, and the number of operating military bases. But Congress has proven to be a stumbling block in these endeavors.
Is the Department of Defense the most efficient spender?
The Department of Defense is not the most efficient spender out there, and they know this. About a third of their budget is spent on just maintaining equipment and personnel. By 2024, rising retirement costs are predicted to soak up the DoD’s budget completely. In their efforts to save money, the DoD could and should reduce spending in personnel and maintenance, such as the number of civilians it employs, the amount of benefits per soldier, and the number of operating military bases. But Congress has proven to be a stumbling block in these endeavors. For one, they’re hesitant to shut down military bases because it will cost the locale numerous jobs. They’re also hesitant to approve pay cuts, afraid it will discourage people from joining the military and therefore cripple our national security; the same goes for downsizing the military, which is another way the DoD could improve its budget.
What percentage of the federal budget is Medicare?
Social Security alone comprises more than a third of mandatory spending and around 23 percent of the total federal budget. Medicare makes up an additional 23 percent of mandatory spending and 15 percent of the total federal budget.
What are the three groups of federal spending?
The U.S. Treasury divides all federal spending into three groups: mandatory spending, discretionary spending and interest on debt. Mandatory and discretionary spending account for more than ninety percent of all federal spending, and pay for all of the government services and programs on which we rely.
How much did tax breaks cost in 2015?
Tax breaks are expected to cost the federal government $1.22 trillion in 2015 - more than all discretionary spending in the same year. Unlike discretionary spending, which must be approved by lawmakers each year during the appropriations process, tax breaks do not require annual approval.
What is spending in the tax code?
Spending in the Tax Code. When the federal government spends money on mandatory and discretionary programs, the U.S. Treasury writes a check to pay the program costs. But there is another type of federal spending that operates a little differently.
What is mandatory spending?
Mandatory spending is spending that Congress legislates outside of the annual appropriations process, usually less than once a year. It is dominated by the well-known earned-benefit programs Social Security and Medicare.
What is discretionary spending?
Discretionary spending refers to the portion of the budget that is decided by Congress through the annual appropriations process each year. These spending levels are set each year by Congress.
What does it mean when the government issues a tax break?
When the government issues a tax break, it chooses to give up tax revenue for a specific purpose - so both spending and tax breaks mean less money in the U.S. Treasury, and both reflect spending priorities laid out by Congress in various pieces of legislation.
What percentage of Medicare is from the federal government?
The federal government’s general fund has been playing a larger role in Medicare financing. In 2019, 43 percent of Medicare’s income came from the general fund, up from 25 percent in 1970. Looking forward, such revenues are projected to continue funding a major share of the Medicare program.
What percentage of Medicare is hospital expenditure?
Hospital expenses are the largest single component of Medicare’s spending, accounting for 40 percent of the program’s spending. That is not surprising, as hospitalizations are associated with high-cost health episodes. However, the share of spending devoted to hospital care has declined since the program's inception.
What percentage of Medicare is home health?
Medicare is a major player in our nation's health system and is the bedrock of care for millions of Americans. The program pays for about one-fifth of all healthcare spending in the United States, including 32 percent of all prescription drug costs and 39 percent of home health spending in the United States — which includes in-home care by skilled nurses to support recovery and self-sufficiency in the wake of illness or injury. 4
How much of Medicare was financed by payroll taxes in 1970?
In 1970, payroll taxes financed 65 percent of Medicare spending.
How is Medicare self-financed?
One of the biggest misconceptions about Medicare is that it is self-financed by current beneficiaries through premiums and by future beneficiaries through payroll taxes. In fact, payroll taxes and premiums together only cover about half of the program’s cost.
What are the benefits of Medicare?
Medicare is a federal program that provides health insurance to people who are age 65 and older, blind, or disabled. Medicare consists of four "parts": 1 Part A pays for hospital care; 2 Part B provides medical insurance for doctor’s fees and other medical services; 3 Part C is Medicare Advantage, which allows beneficiaries to enroll in private health plans to receive Part A and Part B Medicare benefits; 4 Part D covers prescription drugs.
How is Medicare funded?
Medicare is financed by two trust funds: the Hospital Insurance (HI) trust fund and the Supplementary Medical Insurance (SMI) trust fund. The HI trust fund finances Medicare Part A and collects its income primarily through a payroll tax on U.S. workers and employers. The SMI trust fund, which supports both Part B and Part D, ...
What percentage of GDP was spent on welfare in 2015?
But welfare entitlement spending in 2015 is 15.2 percent of GDP. Which is to say, broadly defined welfare spending alone is equal to 86 percent of all the federal taxes that are going to be collected this year.
What percentage of the US economy was welfare in 1957?
That leaves us with the welfare category, the only area of federal spending that has grown significantly relative to the size of the U.S. economy. In 1957, it was 3.9 percent of GDP—not insignificant, to be sure; that’s a slightly larger figure than our present-day military spending.
What percentage of GDP did we spend in 1957?
In 1957, we spent 1 percent of GDP on physical resources; today, we spend a bit less, 0.8 percent of GDP. Other functions constituted 1.6 percent of GDP in 1957, today down to 1.1 percent of GDP. Undistributed receipts is nearly unchanged, up 0.1 percent of GDP. That leaves us with the welfare category, the only area of federal spending ...