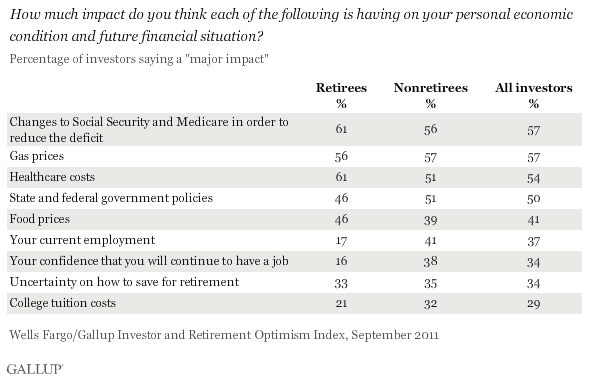
Medicare Rights supports efforts to meaningfully reduce drug prices and lower costs for both people with Medicare and the program as a whole.
Full Answer
What are the strategic goals of the Affordable Care Act?
Medicare Rights supports efforts to meaningfully reduce drug prices and lower costs for both people with Medicare and the program as a whole. Potentially effective strategies include allowing Medicare to negotiate drug prices, increasing pricing transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain, and imposing limits on beneficiary out-of-pocket spending.
Is Medicare an element of Public Policy?
· All told, the economic downturn explained 14% of the Medicare spending slowdown between 2009-2012, or about $4 billion. That's about 0.25% of total traditional Medicare spending (excluding Medicare Advantage and Part D). This estimate fills in some of the gap left by the analysis by Chapin White, Juliette Cubanski, and Tricia Neuman, which ...
Why did Medicare pass in 1965?
At the same time, the health care system is moving towards value-based or alternative payment models, which tie payment to the quality and efficiency of health care delivered. These models are in place in nearly all Medicare settings, including in hospitals, outpatient settings, and post-acute facilities. In order to align Medicare payments and ensure value-based purchasing programs …
What are the strategic goals of the United States of America?
· Eliminating the program's excess costs is an obvious goal for Medicare reform. Medicare's projected total excess costs reflect the extent to which Medicare funds promised benefits by drawing on...
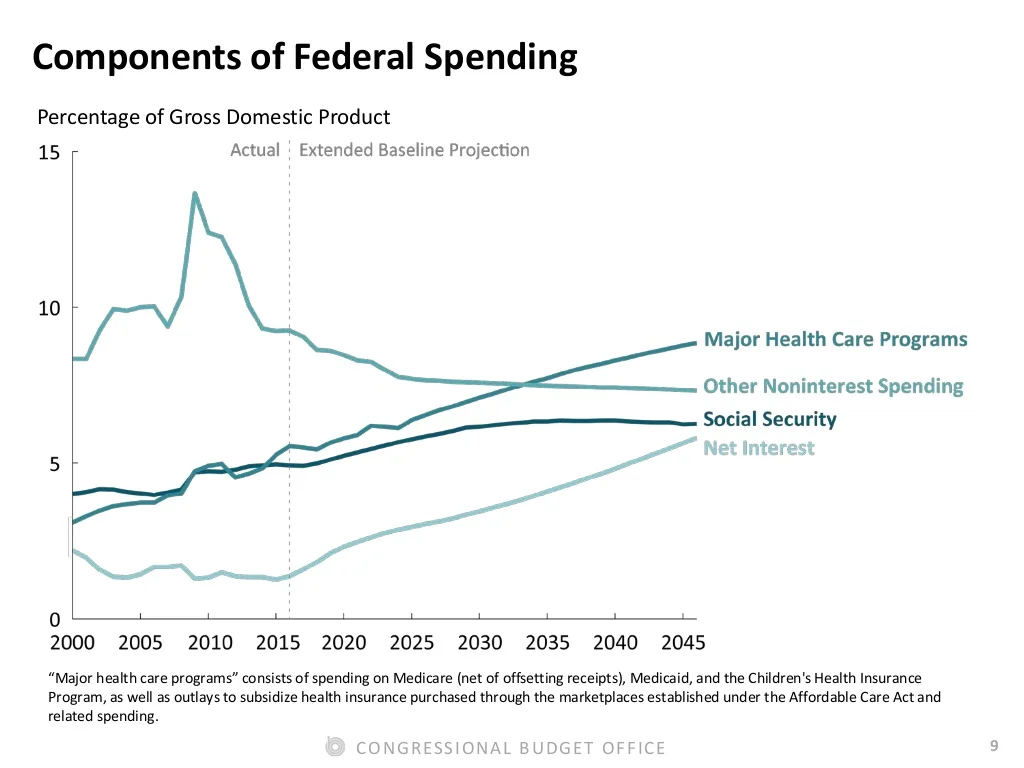
What are social economic goals?
Introduction. All economic systems strive to achieve a set of broad social goals, including economic efficiency, equity, freedom, growth, security, and stability. How these goals are prioritized—and how successful an economy is at attaining these goals—influences the quality of life for all its citizens.
How does Medicare benefit the economy?
Increased availability of 'good jobs' Medicare for All could increase job quality substantially by making all jobs “good” jobs in terms of health insurance coverage and by increasing the potential for higher wages.
What are the 7 economic and social goals?
The broad goals viewed as central to the U.S. economy are stability, security, economic freedom, equity, economic growth, efficiency, and full employment.
What are the 6 social economic goals?
In this lesson, students learn about broad social goals: economic efficiency, economic equity, economic freedom, economic growth, economic security, and economic stability.
What does Medicare mean in economics?
Medicare is a national healthcare program funded by the U.S. government. Congress created the program as part of amendments to the Social Security Act in 1965 to give coverage to people ages 65 and older who didn't have any health insurance.
What is the objective of Medicare?
Medicare's purpose is to provide national health coverage to the following: Older adults, age 65 and over. This has been a traditional retirement age, when health insurance coverage through an employer might typically end.
What are the 5 socio economic goals?
The five economic goals of full employment, stability, economic growth, efficiency, and equity are widely considered to be beneficial and worth pursuing. Each goal, achieved by itself, improves the overall well-being of society. Greater employment is typically better than less.
What are social goals examples?
10 Examples of Social GoalsBe a Volunteer. ... Donate a Portion of Your Income to Charity. ... Join an Advocacy Group to Reduce Carbon Emissions. ... Become a Mentor. ... Attend Community Meetings. ... Request Charitable Donations on Your Birthdays. ... Coach a Youth Sports Team. ... Donate Your Old Clothes.More items...
How many economic and social goals are there?
Analyze how each type of system answers the three economic questions and meets the broad social and economic goals of freedom, security, equity, growth, efficiency, price stability, full employment, and sustainability.
What are the 8 economic goals?
ECONOMIC GOALS The following is a list of the major economic goals: 1) economic growth, 2) price level stability, 3) economic efficiency, 4) full employment, 5) balanced trade, 6) economic security, 7) equitable distribution of income, and 8) economic freedom.
What are the 6 economic goals from most important to least?
Answer and Explanation: The U.S. six economic objectives comprise economic freedom, economic growth, efficiency, and full employment, security, and stability.
What are the 4 major activities that economics and what is its ultimate goal?
There are four major goals of economic policy: stable markets, economic prosperity, business development and protecting employment.
How does Medicare and Medicaid affect the US economy?
Historical NHE, 2020: NHE grew 9.7% to $4.1 trillion in 2020, or $12,530 per person, and accounted for 19.7% of Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Medicare spending grew 3.5% to $829.5 billion in 2020, or 20 percent of total NHE. Medicaid spending grew 9.2% to $671.2 billion in 2020, or 16 percent of total NHE.
How does Medicare affect us today?
Providing nearly universal health insurance to the elderly as well as many disabled, Medicare accounts for about 17 percent of U.S. health expenditures, one-eighth of the federal budget, and 2 percent of gross domestic production.
What impact did Medicare have?
Medicare and Medicaid have greatly reduced the number of uninsured Americans and have become the standard bearers for quality and innovation in American health care. Fifty years later, no other program has changed the lives of Americans more than Medicare and Medicaid.
How Medicare for all would hurt the economy?
The real trouble comes when Medicare for all is financed by deficits. With government borrowing, universal health care could shrink the economy by as much as 24% by 2060, as investments in private capital are reduced.
How does Medicare Rights work?
Medicare Rights supports efforts to meaningfully reduce drug prices and lower costs for both people with Medicare and the program as a whole. Potentially effective strategies include allowing Medicare to negotiate drug prices, increasing pricing transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain, and imposing limits on beneficiary out-of-pocket spending. Changes to the current system must be carefully considered and only adopted if they do not threaten to undermine beneficiary protections or access to medications, such as by weakening the protected classes or introducing additional, inappropriate utilization management strategies.
Can everyone buy Medicare?
Though Medigaps help a growing number of people with Original Medicare afford needed care, not everyone is eligible to buy the plans, and most are only guaranteed the right to do so during very limited time frames.
Does Medicare have an out-of-pocket maximum?
Original Medicare and Part D have no out-of-pocket maximums, exposing beneficiaries to limitless financial risk. While Medicare Advantage (MA) plans do include an out-of-pocket maximum in their benefit packages, this threshold is too high—permitting costs up to $6,700 in 2019.
How did the Great Recession affect Medicare?
Consider, for instance, how much the economic downturn during and since the Great Recession affected Medicare spending growth. One might theorize that it hardly affected it at all because the vast majority of Medicare beneficiaries are retired, so they shouldn't be affected by rising unemployment rates, and they aren't at risk of losing job-related coverage. Also, even if the economy did affect beneficiaries' financial status, after accounting for secondary coverage and supplemental policies, many Medicare beneficiaries face little cost sharing.
What is the effect of increasing enrollment in Medicare Advantage?
One factor left out of the analysis by Dranove et al. is the effect of the increasing enrollment in Medicare Advantage. Their measure of spending was for traditional Medicare only. Medicare Advantage enrollment grew through the recession, and MA plans are paid at a rate that's above average traditional Medicare spending. The price sensitivity experienced by Medicare beneficiaries that explains how the economy affects traditional Medicare spending is also an explanation for growing MA enrollment. MA plans offer coverage of more services for lower out-of-pocket cost.
How much of Medicare was slowed down in 2012?
All told, the economic downturn explained 14% of the Medicare spending slowdown between 2009-2012, or about $4 billion. That's about 0.25% of total traditional Medicare spending (excluding Medicare Advantage and Part D).
Does the economy affect Medicare?
In any case, the new study's finding that the economy does affect Medicare spending is in conflict with some prior work, noted above. It's possible that differences in years analyzed account for differences across studies. However, even if (or when) a slower economy does contribute to lower Medicare spending, the relationship is a lot weaker than for the working-age, privately insured population.
Does Medicare use the business cycle?
the use of Medicare services by beneficiaries has not, on average over the past few decades, moved in concert with the business cycle. In addition, we find no evidence of a relationship between sudden declines in the value of elderly beneficiaries’ assets or their income and their use of health care. We do not, therefore, attribute the difference in spending growth between the two study periods to the recession’s effect on unemployment, lost income, or declines in the values of beneficiaries’ assets.
Why is affordability important in healthcare?
Americans often have to choose between spending a higher proportion of wages on healthcare and paying for other household essentials. Without timely access to healthcare services, Americans risk worsening healthcare outcomes and higher costs. Yet for many, costs make healthcare out of reach.
What is Medicare Part D coverage gap?
Reduce the average out-of-pocket share of prescription drug costs while in the Medicare Part D Prescription Drug Benefit coverage gap for non–Low-Income Subsidy Medicare beneficiaries who reach the gap and have no supplemental coverage in the gap
What is the HHS working on?
Through surveillance, antibiotic stewardship, diagnostic innovations, and research strategies, HHS is working to combat antibiotic-resistant bacteria. HHS also focuses on three key drug classes—anticoagulants, diabetes, and opioids—to prevent adverse drug events.
What is HHS's alternative payment model?
HHS tests and evaluates alternative payment models that bring together private payers, healthcare providers, State partners, consumer groups, beneficiaries, and others. These models aim to reduce costs and improve the quality of care for beneficiaries, including those in at-risk populations.
What is HHS insurance?
HHS is providing guidance, resources, and flexibility for States to enable them to construct competitive, affordable insurance options that best meet the needs of their citizens.
What are the consequences of poor healthcare quality and safety?
The immediate consequences of poor quality and safety include healthcare-associated infections, adverse drug events, and antibiotic resistance.
Why is poor health important?
For a nation to thrive, its population must be healthy. Poor health reduces one’s ability to attend school, care for one’s family, or work. Without healthcare services—including physical, behavioral, and oral healthcare—to help improve health, Americans are at greater risk of poor health and human services outcomes.
How does poverty affect health?
The social and health impacts of poverty can include reduced access to nutritious food; fewer educational opportunities and poor educational outcomes; a lack of access to safe and stable housing; increased risk of poor health outcomes including obesity and heart disease; and difficulty obtaining work opportunities.
What is Strategic Objective 3.2?
Strategic Objective 3.2: Safeguard the public against preventable injuries and violence or their results
How long does it take to increase the percentage of refugees who are self-sufficient?
Increase the percentage of refugees who are self-sufficient (not dependent on any cash assistance) within the first six months of the service period
What was the poverty rate in 2016?
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the official poverty rate in 2016 was 12.7 percent, down 0.8 percentage points from 13.5 percent in 2015. Both the percentage of the U.S. population in poverty and the unemployment rate have declined in the last three years.
Why is it important to have social support after serving time?
Job training and social supports are imperative for ensuring that these individuals are able to reintegrate into their communities.
What is the purpose of the TANF program?
Promote innovation in the TANF program to advance the objective of helping families in need find stability and support through the employment and economic independence of adult participants and the healthy development of children whose families receive assistance
What is Medicare Advantage?
Medicare Advantage health plans contract with community-based organizations and companies to provide falls prevention services. Research has shown Medicare Advantage beneficiaries with access to programs such as SilverSneakers report better emotional and physical health, with fewer limitations in activities of daily living to help keep people safe at home.
How does nutrition affect Medicare?
Older adults are at risk of malnutrition and can become more nutritionally vulnerable when recovering from a hospitalization. It is estimated that 50 percent of the seniors who enter the hospital are already malnourished when they arrive.23 Seniors experiencing hunger are three times more likely to suffer from depression, 50 percent more likely to have diabetes, and 60 percent more likely to have congestive heart failure or a heart attack compared to their peers who do not experience hunger.24Home-delivered meal programs have been found to improve diet quality and increase nutrient intake, while keeping older adults out of more expensive sites of care like the hospital and nursing homes.25 26 27 In addition to fewer inpatient admissions, beneficiaries of food delivery programs reported fewer falls, and lower medical spending, illustrating the positive impact of nutritious food on health outcomes for vulnerable patients.28
What is the uniformity rule for Medicare Advantage?
The uniformity rule requires that Medicare Advantage health plans offer uniform benefits and cost-sharing to all enrollees in a given plan. However, beginning in 2019, health plans may target certain benefits to specific subsets of enrollees in the health plan, as long as the group of enrollees meet objective, measurable medical criteria. For example, a health plan may provide patients with diabetes access to low- or no-cost transportation and/or reduced or eliminated copays for visits to the endocrinologist. To comply with the uniformity rule, these targeted benefits must be offered to every enrollee with a similar diabetes diagnosis. These types of additional flexibilities are designed to enable Medicare Advantage health plans to implement innovative ways to eliminate barriers that prevent beneficiaries with chronic conditions from utilizing necessary, high-value care essential to treating their conditions and improving their health.
What is care management in Medicare?
Care management is a team-based, patient-centered approach designed to assist patients in managing medical conditions more effectively. The financial framework of risk-based, capitated payments under Medicare Advantage offers the opportunity to improve care delivery through the provision of care management to better meet patient needs and improve outcomes. Successful Medicare Advantage-driven care management programs depend on access to real-time, robust data resources to identify high-need patients from integrated electronic health records and payer data.
Does Medicare Advantage provide food?
Currently Medica re Advantage beneficiaries may receive nutritious meals post-surgery or hospitalization. Greg from Kentucky said his Medicare Advantage health plan provided him with food and follow-up contact after surgery and rehabilitation. Nutrition programs that would serve patients in other circumstances are also being developed through Medicare Advantage.
Is Medicare Advantage a V-BID?
CMS recognized the potential of V-BID strategies in Part C by recently reinterpreting the benefit uniformity requirements beginning in plan year 2019 but stopped short of enabling Medicare Advantage health plans to utilize the same V-BID flexibilities in Part D. Congress should instruct CMS to leverage the success of V-BID strategies in Part D, particularly for integrated MA-PD health plans. V-BID has the potential to realize billions in cost savings, while improving treatment and outcomes, particularly for beneficiaries with multiple chronic conditions. Expanding V-BID to Part D for MA-PD health plans has the potential to realize cost savings for consumers, while improving quality across the health care system.
Introduction
It is not difficult to characterize Medicare as an element of public policy. The program launched and legitimated a major role for the Federal Government in funding health care for part of the population—a role that had been highly controversial before.
Health Politics, 1965
The enactment of Medicare in 1965 coincided with several favorable political and economic conditions. This proposition states a correlation: To contend that Medicare passed because these factors converged would be too strong and essentially unprovable.
What Next?
In the quest to reshape the health care system, the sphere “of purposive social action” is much smaller than reformers admit. Many forces that inhibit health reform operate outside the health system per se and have little directly to do with it.
Why must government regulations during economic depressions be lifted?
b. Government regulations during economic depressions must be lifted because they destroy the already slim profit margin.
Which party has supported cuts in social spending?
e. Democrats in recent decades have supported cuts in social spending.
What do Republicans believe about government spending?
d. Republicans believe that government spending is wasteful and puts a drag on the economy.
Can benefits be spread widely in response to many demands?
a. They can be treated as benefits that can be spread widely in response to many demands.
