Funding for Medicare is done through payroll taxes and premiums paid by recipients. Medicaid
Medicaid
Medicaid in the United States is a federal and state program that helps with medical costs for some people with limited income and resources. Medicaid also offers benefits not normally covered by Medicare, including nursing home care and personal care services. The Health Insurance As…
Full Answer
How is Medicare and Medicaid funded?
Medicaid is funded by the federal government and each state. Both programs received additional funding as part of the fiscal relief package in response to the 2020 economic crisis. Medicare is administered by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), a component of the Department of Health and Human Services.
What is Medicare and how does it work?
Medicare is a federal health insurance program that funds hospital and medical care for older people in the U.S. Some people with disabilities also benefit from Medicare. The program consists of:
How much does the government spend on Medicare?
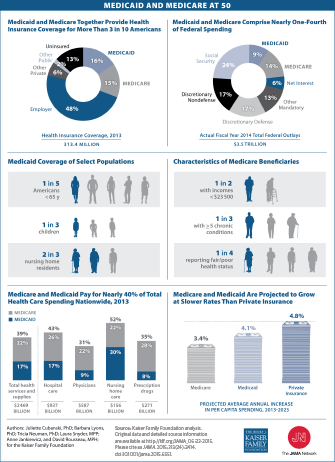
In fact, payroll taxes and premiums together only cover about half of the program’s cost. Medicare is the second largest program in the federal budget: 2020 Medicare expenditures, net of offsetting receipts, totaled $776 billion — representing 12 percent of total federal spending.
How does Medicaid affect the state and federal budgets?
Because of Medicaid’s joint financing structure, the program plays a role in both state and federal budgets. Medicaid plays a unique role in state budgets, acting as both an expenditure and the largest source of federal revenues to states.
How is Medicare being funded?
Funding for Medicare, which totaled $888 billion in 2021, comes primarily from general revenues, payroll tax revenues, and premiums paid by beneficiaries (Figure 1). Other sources include taxes on Social Security benefits, payments from states, and interest.
Is Medicare funded by the federal government?
As a federal program, Medicare relies on the federal government for nearly all of its funding. Medicaid is a joint state and federal program that provides health care coverage to beneficiaries with very low incomes. It relies on both state and federal funds for financing.
What is the purpose of the Medicare Medicaid program?
Medicare is a federal program that provides health coverage if you are 65+ or under 65 and have a disability, no matter your income. Medicaid is a state and federal program that provides health coverage if you have a very low income.
How is Medicaid funded in the US?
The primary source of funding for the non-federal share comes from state general fund appropriations. States also fund the non-federal share of Medicaid with “other state funds” which may include funding from local governments or revenue collected from provider taxes and fees.
What happens when Medicare runs out of money?
It will have money to pay for health care. Instead, it is projected to become insolvent. Insolvency means that Medicare may not have the funds to pay 100% of its expenses. Insolvency can sometimes lead to bankruptcy, but in the case of Medicare, Congress is likely to intervene and acquire the necessary funding.
What are the disadvantages of Medicaid?
Disadvantages of Medicaid They will have a decreased financial ability to opt for elective treatments, and they may not be able to pay for top brand drugs or other medical aids. Another financial concern is that medical practices cannot charge a fee when Medicaid patients miss appointments.
How is Medicaid funded quizlet?
Medicaid is funded thru personal income, corporate and excise taxes. Federal and state support is shared based on the states per capita income. All state Medicaid operations must be approved by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid services. The Medicaid program reimburses providers directly.
Who paid for Medicare?
Medicare is funded by the Social Security Administration. Which means it's funded by taxpayers: We all pay 1.45% of our earnings into FICA - Federal Insurance Contributions Act - which go toward Medicare.
How does the funding of Medicaid differ from the funding for Medicare?
Medicare is federally administered and covers older or disabled Americans, while Medicaid operates at the state level and covers low-income families and some single adults. Funding for Medicare is done through payroll taxes and premiums paid by recipients. Medicaid is funded by the federal government and each state.
Why does Medicare cost so much?
Medicare Part B covers doctor visits, and other outpatient services, such as lab tests and diagnostic screenings. CMS officials gave three reasons for the historically high premium increase: Rising prices to deliver health care to Medicare enrollees and increased use of the health care system.
How much does Medicare cost the government?
$776 billionMedicare accounts for a significant portion of federal spending. In fiscal year 2020, the Medicare program cost $776 billion — about 12 percent of total federal government spending. Medicare was the second largest program in the federal budget last year, after Social Security.
What is the difference between Medicare and Medicaid?
The difference between Medicaid and Medicare is that Medicaid is managed by states and is based on income. Medicare is managed by the federal government and is mainly based on age. But there are special circumstances, like certain disabilities, that may allow younger people to get Medicare.
Where does Medicare money come from?
Most of the funding for Medicare comes from: payroll taxes under the Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA) the Self-Employment Contributions Act (SECA) Typically, the employee pays half of this tax, and the employer pays the other half.
What is the difference between Medicare and Medicaid?
Medicare and Medicaid are two government programs that provide medical and other health-related services to specific individuals in the United States. Medicaid is a social welfare or social protection program , while Medicare is a social insurance program. President Lyndon B. Johnson created both Medicare and Medicaid when he signed amendments ...
What is Medicare Part C?
Medicare Part C. Medicare Part C, also known as Medicare Advantage Plans or Medicare+ Choice, allows users to design a custom plan that suits their medical situation more closely. Part C plans provide everything in Part A and Part B, but may also offer additional services, such as dental, vision, or hearing treatment.
How many people are eligible for both medicaid and medicare?
Dual eligibility. Some people are eligible for both Medicaid and Medicare. Currently, 12 million people have both types of cover, including 7.2 million older adults with a low income and 4.8 million people living with a disability. This accounts for over 15% of people with Medicaid enrolment.
How many people are covered by Medicare?
Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), oversee both. Data on Medicaid show that it serves about 64.5 million people, as of November 2019. Medicare funded the healthcare costs ...
What is the federal reimbursement rate for Medicaid?
This Federal Medical Assistance Percentage (FMAP) changes each year and depends on the state’s average per capita income level. The reimbursement rate begins at 50% and reaches 77% in 2020.
How many people in the US have health insurance?
The CMS report that around 90% of the U.S. population had medical insurance in 2018. According to the 2017 U.S. census, 67.2% of people have private insurance, while 37.7 percent have government health coverage.
How much of the federal government is funding Medicaid expansion?
The federal government provided additional funds to states undergoing Medicaid expansion, paying 100 percent of Medicaid expansion costs through 2016 and 90 percent of those costs through 2020. All states, whether or not they participate in Medicaid expansion, continue to receive federal funding from these three sources:
How much does the federal government match for Medicaid?
For every $1 a state pays for Medicaid, the federal government matches it at least 100%, i.e., dollar for dollar. The more generous a state is in covering people, the more generous the federal government is required to be. There is no defined cap, and federal expenditures increase based on a state's needs.
What is the GOP's plan for 2020?
Healthy Adult Opportunity. The GOP aims to decrease how much federal money is spent on Medicaid. The 2020 Fiscal Year budget 6 proposed cutting Medicaid by $1.5 trillion over the next decade but the budget failed to pass.
How much does Medicaid pay for health care?
According to the American Hospital Association, hospitals are paid only 87 cents for every dollar spent by the hospital to treat people on Medicaid. 2
When did the FMAP increase?
The Affordable Care Act increased the enhanced FMAP for states from October 1, 2015 through September 30, 2019. It did so by 23 percentage points but did not allow any state to exceed 100%. For Fiscal Year 2020, the enhanced matching rates will be lower.
Which states have 50% FMAP?
Alaska, California, Colorado, Connecticut, Maryland, Massachusetts, Minnesota, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, North Dakota, Virginia, Washington, and Wyoming are the only states to have an FMAP of 50% for Fiscal Year 2020 (October 1, 2019 through September 30, 2020). All other states receive a higher percentage of Medicaid funds from ...
Who is excluded from Medicaid expansion?
Specifically, adults on Medicaid expansion or adults less than 65 years old without disabilities or long-term care placement needs would be affected. Pregnant women and low-income parents would be excluded. States could require asset tests for these individuals, propose work requirements, and/or require cost-sharing.
How is Medicaid funded?
The Medicaid program is jointly financed by the federal and state governments with contributions governed by the FMAP formula that has remained largely unchanged over the program’s 50 year history. The federal/state matching arrangement provides a financing structure that is responsive to changes in enrollment and program needs, enabling states to adjust program expenditures in response to economic and policy changes. A program as large as Medicaid will always be a focus of budget scrutiny at the state and federal levels. Changes to Medicaid’s financing structure would have implications for states, the federal government and beneficiaries which would warrant careful analysis.
Who is funding the Medicaid program?
The Medicaid program is jointly funded by states and the federal government. There has been renewed interest in how Medicaid is financed in light of the additional federal financing for the Medicaid expansion under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) as well as ongoing budget discussions at the federal level. This brief reviews how the Medicaid program ...
What is Medicaid DSH?
DSH, or “disproportionate share” hospitals are hospitals that serve a large number of Medicaid and low-income uninsured patients. 9 In many states, DSH payments have been crucial to the financial stability of “safety net” hospitals. Federal DSH payments totaled $16.4 billion in FFY 2013. 10 While states have considerable discretion in determining the amount of DSH payments to each DSH hospital, their discretion is bounded by two caps – one at the state level, and the other at the facility level. At the state level, the total amount of federal funds that each state can spend on DSH is specified in an annual DSH allotment for each state. While there have been some special adjustments, the DSH allotments are generally calculated based on the previous year’s allotment increased by inflation but then subject to a cap of 12 percent of the total amount of Medicaid expenditures under the state plan that fiscal year. When the DSH caps were originally set, they locked in variation across states in DSH spending. At the facility level, Medicaid DSH payments are limited to 100 percent of the costs incurred for serving Medicaid and uninsured patients that have not been compensated by Medicaid (Medicaid shortfall).
How does Medicaid affect the state budget?
While Medicaid is the third largest domestic program in the federal budget following Medicare and Social Security, the program plays a unique role in state budgets. As a result of the joint financing structure, Medicaid acts as both an expenditure and the largest source of federal revenue in state budgets. Unlike at the federal level, states are required to regularly balance their budgets, making decisions about spending across programs as well as how much revenue to collect. Balancing these competing priorities creates an ever present tension. Unlike other programs, state spending on Medicaid brings in federal revenues due to its financing structure. The implementation of the major ACA coverage expansions in 2014 led to higher enrollment and total overall spending growth in Medicaid; however, with full federal financing of the expansion, state Medicaid spending grew at a slower pace. Early evidence from states that have adopted the Medicaid expansion also indicates there are state budget savings both within Medicaid budgets and outside of Medicaid.
What is Medicaid in economic downturn?
During economic downturns, individuals lose jobs, incomes decline and more people qualify and enroll in Medicaid which increases program spending at the same time as state revenues decline, making it difficult for states to match rising expenditures.
How does the economy affect Medicaid?
The economy has a strong effect on Medicaid enrollment and therefore spending. Medicaid spending and enrollment are affected by a number of factors – health care inflation, policy changes, etc. However, one of the largest drivers of Medicaid spending and enrollment trends is changes in economic conditions. Medicaid is a countercyclical program. During economic downturns, individuals lose jobs, incomes decline and more people qualify and enroll in Medicaid which increases program spending. As economic conditions improve, Medicaid enrollment and spending growth tend to slow.
Why is Medicaid important?
Because of Medicaid’s joint financing structure, the program plays a role in both state and federal budgets. Medicaid plays a unique role in state budgets, acting as both an expenditure and the largest source of federal revenues to states.
How is Medicare funded?
How Medicare Is Funded. Medicare is funded by two trust funds that can only be used for Medicare. The hospital insurance trust fund is funded by payroll taxes paid by employees, employers, and the self-employed. These funds are used to pay for Medicare Part A benefits. 11 .
How is Medicare supplemental insurance fund funded?
Medicare's supplementary medical insurance trust fund is funded by Congress, premiums from people enrolled in Medicare, and other avenues, such as investment income from the trust fund. These funds pay for Medicare Part B benefits, Part D benefits, and program administration expenses.
How much did Medicare spend in 2019?
If we look at each program individually, Medicare spending grew 6.7% to $799.4 billion in 2019, which is 21% of total NHE, while Medicaid spending grew 2.9% to $613.5 billion in 2019, which is 16% of total NHE. 3 . The CMS projects that healthcare spending is estimated to grow by 5.4% each year between 2019 and 2028.
What is CMS and Medicaid?
CMS works alongside the Department of Labor (DOL) and the U.S. Treasury to enact insurance reform. The Social Security Administration (SSA) determines eligibility and coverage levels. Medicaid, on the other hand, is administered at the state level.
What is Medicare contribution tax?
It is known as the unearned income Medicare contribution tax. Taxpayers in this category owe an additional 3.8% Medicare tax on all taxable interest, dividends, capital gains, annuities, royalties, and rental properties that are paid outside of individual retirement accounts or employer-sponsored retirement plans .
What is the Medicare tax rate for 2013?
On Jan. 1, 2013, the ACA also imposed an additional Medicare tax of 0.9% on all income above a certain level for high-income taxpayers. Single filers have to pay this additional amount on all earned income they receive above $200,000 and married taxpayers filing jointly owe it on earned income in excess of $250,000.
What is Medicare 2021?
Updated Jun 29, 2021. Medicare, and its means-tested sibling Medicaid, are the only forms of health coverage available to millions of Americans today. They represent some of the most successful social insurance programs ever, serving tens of millions of people including the elderly, younger beneficiaries with disabilities, ...
How is Medicare funded?
Medicare is financed by two trust funds: the Hospital Insurance (HI) trust fund and the Supplementary Medical Insurance (SMI) trust fund. The HI trust fund finances Medicare Part A and collects its income primarily through a payroll tax on U.S. workers and employers. The SMI trust fund, which supports both Part B and Part D, ...
What percentage of Medicare is from the federal government?
The federal government’s general fund has been playing a larger role in Medicare financing. In 2019, 43 percent of Medicare’s income came from the general fund, up from 25 percent in 1970. Looking forward, such revenues are projected to continue funding a major share of the Medicare program.
What percentage of Medicare is home health?
Medicare is a major player in our nation's health system and is the bedrock of care for millions of Americans. The program pays for about one-fifth of all healthcare spending in the United States, including 32 percent of all prescription drug costs and 39 percent of home health spending in the United States — which includes in-home care by skilled nurses to support recovery and self-sufficiency in the wake of illness or injury. 4
How much of Medicare was financed by payroll taxes in 1970?
In 1970, payroll taxes financed 65 percent of Medicare spending.
How is Medicare self-financed?
One of the biggest misconceptions about Medicare is that it is self-financed by current beneficiaries through premiums and by future beneficiaries through payroll taxes. In fact, payroll taxes and premiums together only cover about half of the program’s cost.
What are the benefits of Medicare?
Medicare is a federal program that provides health insurance to people who are age 65 and older, blind, or disabled. Medicare consists of four "parts": 1 Part A pays for hospital care; 2 Part B provides medical insurance for doctor’s fees and other medical services; 3 Part C is Medicare Advantage, which allows beneficiaries to enroll in private health plans to receive Part A and Part B Medicare benefits; 4 Part D covers prescription drugs.
How much did Medicare cost in 2019?
In 2019, it cost $644 billion — representing 14 percent of total federal spending. 1. Medicare has a large impact on the overall healthcare market: it finances about one-fifth of all health spending and about 40 percent of all home health spending. In 2019, Medicare provided benefits to 19 percent of the population. 2.
How long has Medicare and Medicaid been around?
Medicare & Medicaid: keeping us healthy for 50 years. On July 30, 1965, President Lyndon B. Johnson signed into law legislation that established the Medicare and Medicaid programs. For 50 years, these programs have been protecting the health and well-being of millions of American families, saving lives, and improving the economic security ...
When did Medicare expand?
Over the years, Congress has made changes to Medicare: More people have become eligible. For example, in 1972 , Medicare was expanded to cover the disabled, people with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) requiring dialysis or kidney transplant, and people 65 or older that select Medicare coverage.
What is Medicare Part D?
Medicare Part D Prescription Drug benefit. The Medicare Prescription Drug Improvement and Modernization Act of 2003 (MMA) made the biggest changes to the Medicare in the program in 38 years. Under the MMA, private health plans approved by Medicare became known as Medicare Advantage Plans.
What is the Affordable Care Act?
The 2010 Affordable Care Act (ACA) brought the Health Insurance Marketplace, a single place where consumers can apply for and enroll in private health insurance plans. It also made new ways for us to design and test how to pay for and deliver health care.
When was the Children's Health Insurance Program created?
The Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) was created in 1997 to give health insurance and preventive care to nearly 11 million, or 1 in 7, uninsured American children. Many of these children came from uninsured working families that earned too much to be eligible for Medicaid.
Does Medicaid cover cash assistance?
At first, Medicaid gave medical insurance to people getting cash assistance. Today, a much larger group is covered: States can tailor their Medicaid programs to best serve the people in their state, so there’s a wide variation in the services offered.
How is Medicare paid?
Medicare’s Supplementary Medicare Insurance (SMI) is paid by an authorization of Congress (ie: paid by general tax revenues in annual budgets). The amount of payroll taxes withheld for Medicare is 1.45% for employees and 1.45% for employers.
How much is Medicare payroll tax?
The amount of payroll taxes withheld for Medicare is 1.45% for employees and 1.45% for employers. So if you earn say $50,000 a year, that’s $725 ($60.42 per month) in extra payroll taxes an employee and employer each pay annually.
How much did Social Security contribute to the deficit?
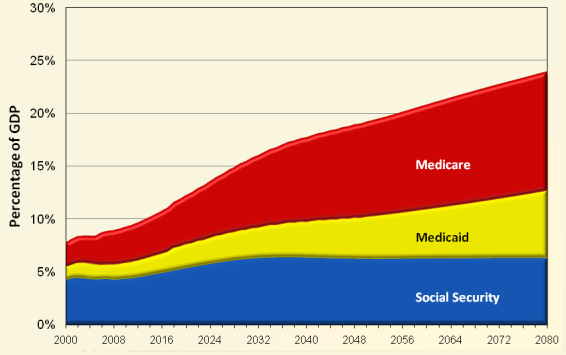
Social Security contributed $73 Billion to the U.S. deficit just in 2014. Social Security is expected to add to the U.S. deficit every year, due mostly in part to the increased retiring of Baby Boomers. Medicare. Medicare composes 15% of the U.S. Budget (2018).
How much is Social Security tax?
Social Security. The Social Security Administration or SSA tax is 12.4% of one’s income (up to $132,900 in wages for 2019) if self-employed. For all employees, 6.2% is paid by the employer, and another 6.2% is taken out of one’s paycheck from the employee in the form of pay roll taxes.
How much unemployment compensation do governors get?
1. Provide up to $400 additional Unemployment Compensation. Requires state governors to chip in $100 per week to receive the full $300 per week from the federal gov. This creates an intensive for state governors.
Is Social Security money taxable?
The SSA then invests the money in U.S. Treasuries in a trust fund. SSA then pays out money each year as taxable benefits. Social Security has remained an ‘off-budget’ item since 1990 and is funded no matter what tax revenues the federal government has.
Can the President change the federal budget?
A president has NO Constitutional authority to change the federal budget signed into law, or order the Treasury to just print and send money. ONLY Congress; and ONLY by way of legislation (a Bill), passing BOTH the House AND Senate, and then signed by a President can change the government’s budget.
How is health insurance funded?
Treasury. The Hospital Insurance Trust Fund is funded by federal payroll taxes and income taxes from Social Security benefits.
What is Medicare Advantage?
Medicare Advantage, a health plan provided by private insurance companies, is paid for by federal funding, subscriber premiums and co-payments. It includes the same coverage as the federal government’s Original Medicare program as well as additional supplemental benefits.
What is Supplementary Medical Insurance Fund?
The Supplementary Medical Insurance Fund is composed of funds approved by Congress and Part B and Part D premiums paid by subscribers.
Is Medicare Advantage financed by monthly premiums?
Each insurance company is approved and contracted by Medicare and must fulfill guidelines for coverage as established by the government. Medicare Advantage plans are also financed by monthly premiums paid by subscribers. The premium amounts vary by company and plan.
Funding
Cost
- Medicaid is not exactly known for being generous when it comes to paying for health care. According to the American Hospital Association, hospitals are paid only 87 cents for every dollar spent by the hospital to treat people on Medicaid. The National Investment Center (NIC) reported that, on average, Medicaid pays only half of what traditional Medicare and Medicare Advantage …
Effects
- Hospitals that care for more people on Medicaid or for people that are uninsured, in the end, are reimbursed far less than facilities that operate in areas where there are more people covered by private insurance. Between 2000 and 2018, at least 85 rural hospitals closed their doors to inpatient care due to low reimbursement rates and other financial concerns.
Causes
- To even out the playing field, Disproportionate Share Hospital (DSH) payments came into effect. Additional federal funds are given to the states to divide amongst eligible hospitals that see a disproportionate number of people with little to no insurance. The idea was to decrease the financial burden to those facilities so that they could continue to provide care to individuals with …
Economy
- Notably, Mississippi has the lowest per capita income level with a 2020 FMAP of 76.98 percent. This means the federal government pays for 76.98 percent of the state's Medicaid costs, contributing $3.34 for every $1 the state spends.
Results
- The Affordable Care Act increased the enhanced FMAP for states from October 1, 2015 through September 30, 2019. It did so by 23 percentage points but did not allow any state to exceed 100 percent. For Fiscal Year 2020, the enhanced matching rates will be lower. The Healthy Kids Act will allow an increase in the enhanced FMAP by 11.5 percent, again not to exceed 100 percent to…
Benefits
- The services covered by enhanced matching rates are seen as valuable because they may help to decrease the burden of healthcare costs in the future. In that way, paying more money upfront is seen as a worthy investment.