Medicaid is targeted at helping the poor and Medicare is broadly focused toward the elderly, but both programs provide aid to Americans for medical expenses. Although there are functional differences between Medicare and Medicaid, many reforms would address both programs in similar ways.
Full Answer
What are entitlement programs?
– Social Security, Medicare & Medicaid Entitlement programs regularly come up during discussions about the American federal budget. Entitlement programs are benefits provided by law if an individual meets the set of requirements laid out as part of the program.
What is Medicare Medicaid and how does it work?
Medicaid is an “entitlement” program, which means that anyone who meets eligibility rules has a right to enroll in Medicaid coverage. It also means that states have guaranteed federal financial support for part of the cost of their Medicaid programs. In order to receive federal funding, states must cover certain “mandatory” populations:
How many Americans are enrolled in both Medicare and Medicaid?
And there is overlap between the two programs: nearly 10 million low-income seniors and people with disabilities — so-called “dual eligibles” — are enrolled in both Medicare and Medicaid.
What is Medicare?
Medicare is an insurance program. Medical bills are paid from trust funds which those covered have paid into. It serves people over 65 primarily, whatever their income; and serves younger disabled people and dialysis patients.

What are the differences between the entitlement programs Medicaid and Medicare?
What are the differences between the entitlement programs Medicaid and Medicare? Medicare provides health care for people over 65, and Medicaid offers benefits for low-income families and individuals.
Is Medicare considered an entitlement program?
The best-known entitlements are the government's major benefit programs, such as Social Security and Medicare.
How are Medicare and Medicaid different and similar?
Medicare is a federal program that provides health coverage if you are 65+ or under 65 and have a disability, no matter your income. Medicaid is a state and federal program that provides health coverage if you have a very low income.
Why is medical An example of an entitlement program?
Medicaid is an “entitlement” program, which means that anyone who meets eligibility rules has a right to enroll in Medicaid coverage. It also means that states have guaranteed federal financial support for part of the cost of their Medicaid programs.
What is considered an entitlement program?
Entitlement programs are either financed from Federal trust funds or paid out of the general revenues. Those paid out of the general revenues are income redistribution programs intended to address problems such as illness and poverty.
What is a entitlement program definition?
Entitlement Programs of the federal government include Medicaid, Medicare, Social Security, Unemployment, and welfare programs. Entitlement programs are rights granted to citizens and certain non-citizens by federal law. The programs are defined as either contributory or non-contributory programs.
What is the difference between the Medicare and Medicaid programs quizlet?
What is the difference between Medicare and Medicaid? Medicare is a federal program that provides health coverage if you are 65 and older or have a severe disability, no matter your income. Medicaid is a state and federal program that provides health coverage if you have a very low income.
What are the disadvantages of Medicaid?
Disadvantages of Medicaid They will have a decreased financial ability to opt for elective treatments, and they may not be able to pay for top brand drugs or other medical aids. Another financial concern is that medical practices cannot charge a fee when Medicaid patients miss appointments.
How does the funding of Medicaid differ from the funding for Medicare?
Medicare is federally administered and covers older or disabled Americans, while Medicaid operates at the state level and covers low-income families and some single adults. Funding for Medicare is done through payroll taxes and premiums paid by recipients. Medicaid is funded by the federal government and each state.
What are entitlement programs give three examples of entitlement programs and explain their purposes?
Entitlement programs are social welfare programs that people are "entitled to" if they meet certain criteria for eligibility. If people meet the criteria, the federal government guarantees assistance for them. Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid are examples of entitlement programs.
What are three examples of entitlement programs what type of spending are they?
Outlays for the nation's three largest entitlement programs (Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid) and for many smaller programs (unemployment compensation, retirement programs for federal employees, student loans, and deposit insurance, for example) are mandatory spending.
Can you have Medicare and Medicaid?
Medicare-Medicaid Plans Medicare is working with some states and health plans to offer demonstration plans for certain people who have both Medicare and Medicaid and make it easier for them to get the services they need. They're called Medicare-Medicaid Plans.
What is Medicare insurance?
Medicare. Medicare is an insurance program. Medical bills are paid from trust funds which those covered have paid into. It serves people over 65 primarily, whatever their income; and serves younger disabled people and dialysis patients. Patients pay part of costs through deductibles for hospital and other costs.
Do you pay for medical expenses on medicaid?
Patients usually pay no part of costs for covered medical expenses. A small co-payment is sometimes required. Medicaid is a federal-state program. It varies from state to state. It is run by state and local governments within federal guidelines.
Is Medicare a federal program?
Small monthly premiums are required for non-hospital coverage. Medicare is a federal program. It is basically the same everywhere in the United States and is run by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, an agency of the federal government.
What is entitlement program?
Entitlement programs are benefits provided by law if an individual meets the set of requirements laid out as part of the program. In the United States, Social Security, Medicare, Medicaid, food stamps, and veterans’ compensation are broadly considered to be entitlement programs. This list is not exhaustive, and there is significant debate about ...
What is single payer health care?
A single-payer system for health care is popular among those on America’s political left, and for 63% of Americans generally. Single-payer health care is when a single public system covers the costs of all essential health care. Some in the U.S. call it Medicare for All.
How much is mandatory spending?
Mandatory spending is the money the government is obligated to pay out each year, on top of which discretionary spending is added. In 2020, Social Security was an expense of almost $1.1 trillion, with Medicare an additional $835 billion and Medicaid at $425 billion, according to the nonpartisan Congressional Budget Office (CBO).
How much money did the government spend on medical bills in 2020?
This is, frankly, a lot of money. These figures mean the federal government paid $1.26 trillion in medical expenses between Medicare and Medicaid in 2020, on top of insurance outlays and personal expenditures.
What does it mean to lessen Social Security?
Lessening the outlay of Social Security without lessening the burden on the individual means people will pay more for less — a politically difficult pill to swallow. Reform, then, must address both the funding and expenses of our entitlement programs by modifying how individual programs work and replacing or cutting funding to others.
How many new claims for unemployment in the US?
In the United States, there have been more than 36 million new claims for unemployment benefits during the coronavirus pandemic. At the same time, an aging population and longer average life spans threaten to deplete the Social Security program’s funding.
When will Social Security run out?
According to recent projections, Social Security funds will run out in 2037, after which incoming taxes will be enough to pay just 76% of scheduled benefits. If that were to happen today, 65 million Americans would see their benefits slashed, leaving many impoverished or worse.
What is entitlement program?
These programs, called entitlements, are a vital support for millions of Americans who need health coverage and income in retirement. These entitlements are also a heavy drag on the U.S. economy. Baby Boomers continue to age out of the workforce and cash in, taking benefits and living longer.
What does Trump say about Medicaid?
Trump argues that the states already run Medicaid programs offer more than the minimum requirements, and that states are better equipped to meet citizens' needs while reducing waste. Democratic presidential nominee Hillary Clinton's stance on Medicaid is to expand the program to more people — and make enrollment easier.
Why did healthcare spending decrease in 2009?
Then, in the midst of the recession, it slowed. From 2009 to 2013, healthcare spending started to decline. This change may be because of efficiencies put in place — think generic drugs and improved payment methods.
How much less is Medicaid spending?
Spending on Medicaid, like healthcare spending for private insurance and Medicare, has slowed in recent years. In fact, Medicaid spending will likely be $1.05 billion less — for the years from 2014 to 2019 — than the government originally forecasted, according to U.S. News.
Why are entitlements in crisis?
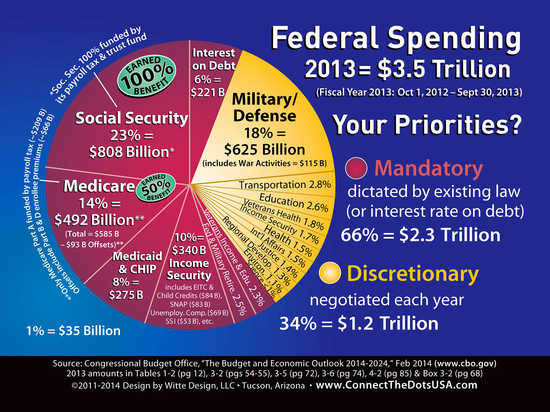
About half of the United States budget goes toward paying Social Security, Medicare and Medicaid. These programs, called entitlements, are a vital support for millions of Americans who need health coverage and income in retirement.
When was Medicare established?
Medicare is a government health insurance program for older and disabled Americans that was established in 1965 . Like Social Security, Medicare faces demographic headwinds as fewer Americans pay into the pot, while more are getting benefits than in the past.
When will Social Security start paying?
Currently Social Security is on track to make timely payments to beneficiaries through 2037, or 21 years from now. That said, the government should probably get around to doing something about Social Security before then. That's because the program will start to cost more than it makes in interest income and taxes by 2020.
How much does the federal government contribute to Medicaid?
The federal government contributes at least $1 in matching funds for every $1 a state spends on Medicaid. The fixed percentage the federal government pays, known as the “FMAP,” varies by state, with poorer states receiving larger amounts for each dollar they spend than wealthier states.
How effective is medicaid?
Medicaid is very effective in providing health insurance coverage to the most vulnerable. Since the ACA’s major coverage expansions took effect in 2014, Medicaid has helped to reduce the number of uninsured from 45 million to 29 million.
Why is Medicaid important?
Medicaid plays an even more important role in insuring low-income Americans due to the Affordable Care Act. As noted, the ACA provides coverage for poor and low-income adults by expanding eligibility for Medicaid to 138 percent of the poverty line.
What is Medicaid insurance?
Created in 1965, Medicaid is a public insurance program that provides health coverage to low-income families and individuals, including children, parents, pregnant women, seniors, and people with disabilities; it is funded jointly by the federal government and the states. Each state operates its own Medicaid program within federal guidelines. Because the federal guidelines are broad, states have a great deal of flexibility in designing and administering their programs. As a result, Medicaid eligibility and benefits can and often do vary widely from state to state.
How many people will be on medicaid by 2029?
By 2029, 14 million more low-income adults will have enrolled in Medicaid and gained access to affordable comprehensive health coverage due to the ACA, CBO estimates. Chart. The expansion is a very good financial deal for states.
How many people are covered by medicaid?
In 2018, Medicaid provided health coverage for 97 million low-income Americans over the course of the year. In any given month, Medicaid served 32 million children, 28 million adults (mostly in low-income working families), 6 million seniors, and 9 million people with disabilities, according to Congressional Budget Office (CBO) estimates.
What percentage of Medicaid is paid by the federal government?
In the poorest states, the federal government pays 73 percent of Medicaid service costs; the national average is between 57 and 60 percent. As noted above, the federal government pays an enhanced 90 percent of service costs on a permanent basis for low-income adults covered by the ACA Medicaid expansion.
Do people pay for Medicare?
Most people do not pay for all of their Medicare benefits, but rather pay for a small portion towards them. The gap between what people pay into Medicare and what they receive in benefits, is, in fact, the largest source of the country’s fiscal problem.
Does Medicare and Social Security contribute to the country's fiscal problems?
According to Leonhardt, there is no reading of the budget that support the liberal view that Social Security and Medicare do not contribute to the country’s fiscal problems . He believes that if they are left unchanged, they will create large deficits.
What is the income related monthly adjustment amount for Medicare?
Individuals with income greater than $85,000 and married couples with income greater than $170,000 must pay a higher premium for Part B and an extra amount for Part D coverage in addition to their Part D plan premium. This additional amount is called income-related monthly adjustment amount. Less than 5 percent of people with Medicare are affected, so most people will not pay a higher premium.
How long do you have to be on Medicare if you are disabled?
Disabled individuals are automatically enrolled in Medicare Part A and Part B after they have received disability benefits from Social Security for 24 months. NOTE: In most cases, if someone does not enroll in Part B or premium Part A when first eligible, they will have to pay a late enrollment penalty.
How long does it take to get Medicare if you are 65?
For someone under age 65 who becomes entitled to Medicare based on disability, entitlement begins with the 25 th month of disability benefit entitlement.
What happens if you don't enroll in Part A?
If an individual did not enroll in premium Part A when first eligible, they may have to pay a higher monthly premium if they decide to enroll later. The monthly premium for Part A may increase up to 10%. The individual will have to pay the higher premium for twice the number of years the individual could have had Part A, but did not sign up.
How long does Medicare take to pay for disability?
A person who is entitled to monthly Social Security or Railroad Retirement Board (RRB) benefits on the basis of disability is automatically entitled to Part A after receiving disability benefits for 24 months.
Why does Part A end?
There are special rules for when premium-free Part A ends for people with ESRD. Premium Part A and Part B coverage can be voluntarily terminated because premium payments are required. Premium Part A and Part B coverage ends due to: Voluntary disenrollment request (coverage ends prospectively); Failure to pay premiums;
When do you have to be on Medicare before you can get Medicare?
Individuals already receiving Social Security or RRB benefits at least 4 months before being eligible for Medicare and residing in the United States (except residents of Puerto Rico) are automatically enrolled in both premium-free Part A and Part B.
