
| Characteristic | Total spending in billion U.S. dollars |
|---|---|
| 2013 | 582.9 |
| 2012 | 574.2 |
| 2011 | 549.1 |
| 2010 | 522.9 |
How much money has been spent on Medicare since 1970?
In 1970, some 7.5 billion U.S. dollars were spent on the Medicare program in the United States. Fifty years later, this figure stood at 925.8 billion U.S. dollars. This statistic depicts total Medicare spending from 1970 to 2020. Medicare is the federal health insurance program in the U.S. for the elderly and those with disabilities.
How much did the US spend on Medicare in 2020?
Total Medicare spending from 1970 to 2020 (in billion U.S. dollars)* Characteristic Total spending in billion U.S. dollars 2020** 925.8 2019 796.1 2018 740.7 2017 710.2 9 more rows ...
What is the average growth rate of Medicare spending?
Medicare per capita spending is projected to grow at an average annual rate of 5.1 percent over the next 10 years (2018 to 2028), due to growing Medicare enrollment, increased use of services and intensity of care, and rising health care prices.
How much was spent on discretionary spending in FY 2010?
Actual Discretionary Spending -This information is from the OMB's FY 2012 budget, which shows how much was actually spent in FY 2010. Discretionary spending was just under budget, at $1.306 billion.
How much did the US spend on healthcare in 2010?
$2.6 trillionTotal US health spending reached $2.6 trillion, or $8,402 per person, in 2010 ( Exhibit 1 ). After historically low growth in 2009, aggregate health care spending in 2010 increased 3.9 percent—only 0.1 percentage point faster than the rate of growth in 2009 (3.8 percent) ( Exhibit 2 ).
How much is spent on Medicare each year?
Historical NHE, 2020: Medicare spending grew 3.5% to $829.5 billion in 2020, or 20 percent of total NHE. Medicaid spending grew 9.2% to $671.2 billion in 2020, or 16 percent of total NHE.
How fast was the spending on Medicare as a percentage of the GDP growing in 2010?
Average annual growth in total Medicare spending was 4.4 percent between 2010 and 2018, down from 9.0 percent between 2000 and 2010, despite faster growth in enrollment since 2011 when the baby boom generation started becoming eligible for Medicare (Figure 4).
How much did the US spend on healthcare in 2011?
$2.7 trillionIn 2011 US health care spending grew 3.9 percent to reach $2.7 trillion, marking the third consecutive year of relatively slow growth.
How much has the cost of healthcare increases in the last 10 years?
The average annual growth in health spending from 2010-2019 was 4.2%.
Is Medicare underfunded?
Politicians promised you benefits, but never funded them.
How fast has spending per person been increasing for Medicare?
Higher Medicare payments per Medicare Advantage enrollee increased total Medicare spending by an estimated $7 billion in 2019. Across the approximately 22 million people enrolled in Medicare Advantage in 2019, higher spending of $321 per person led to about $7 billion in additional spending in that year.
How much of US GDP is spent on healthcare?
19.7%In 2020, U.S. national health expenditure as a share of its gross domestic product (GDP) reached an all time high of 19.7%. The United States has the highest health spending based on GDP share among developed countries. Both public and private health spending in the U.S. is much higher than other developed countries.
Why are Medicare costs rising?
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) announced the premium and other Medicare cost increases on November 12, 2021. The steep hike is attributed to increasing health care costs and uncertainty over Medicare's outlay for an expensive new drug that was recently approved to treat Alzheimer's disease.
How much did the United States spend on healthcare in 2019?
$3.8 trillionUS health care spending increased 4.6 percent to reach $3.8 trillion in 2019, similar to the rate of growth of 4.7 percent in 2018. The share of the economy devoted to health care spending was 17.7 percent in 2019 compared with 17.6 percent in 2018.
How much does the US spend on healthcare 2020?
$4.1 trillionU.S. health care spending grew 9.7 percent in 2020, reaching $4.1 trillion or $12,530 per person. As a share of the nation's Gross Domestic Product, health spending accounted for 19.7 percent.
How much is spent on healthcare in the US annually?
four trillion U.S. dollarsAnnual health expenditures stood at over four trillion U.S. dollars in 2020, and personal health care expenditure equaled 10,202 U.S. dollars per resident. Federal and state government budgets are being further stretched by the coronavirus outbreak, which is pushing health expenditures even higher.
What percentage of Medicare is spending?
Key Facts. Medicare spending was 15 percent of total federal spending in 2018, and is projected to rise to 18 percent by 2029. Based on the latest projections in the 2019 Medicare Trustees report, the Medicare Hospital Insurance (Part A) trust fund is projected to be depleted in 2026, the same as the 2018 projection.
What has changed in Medicare spending in the past 10 years?
Another notable change in Medicare spending in the past 10 years is the increase in payments to Medicare Advantage plans , which are private health plans that cover all Part A and Part B benefits, and typically also Part D benefits.
How is Medicare Financed?
Medicare is funded primarily from general revenues (43 percent), payroll taxes (36 percent), and beneficiary premiums (15 percent) (Figure 7) .
How much does Medicare cost?
In 2018, Medicare spending (net of income from premiums and other offsetting receipts) totaled $605 billion, accounting for 15 percent of the federal budget (Figure 1).
Why is Medicare spending so slow?
Slower growth in Medicare spending in recent years can be attributed in part to policy changes adopted as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the Budget Control Act of 2011 (BCA). The ACA included reductions in Medicare payments to plans and providers, increased revenues, and introduced delivery system reforms that aimed to improve efficiency and quality of patient care and reduce costs, including accountable care organizations (ACOs), medical homes, bundled payments, and value-based purchasing initiatives. The BCA lowered Medicare spending through sequestration that reduced payments to providers and plans by 2 percent beginning in 2013.
What is the average annual growth rate for Medicare?
Average annual growth in total Medicare spending is projected to be higher between 2018 and 2028 than between 2010 and 2018 (7.9 percent versus 4.4 percent) (Figure 4).
What is excess health care cost?
Over the next 30 years, CBO projects that “excess” health care cost growth—defined as the extent to which the growth of health care costs per beneficiary, adjusted for demographic changes, exceeds the per person growth of potential GDP (the maximum sustainable output of the economy)—will account for half of the increase in spending on the nation’s major health care programs (Medicare, Medicaid, and subsidies for ACA Marketplace coverage), and the aging of the population will account for the other half.
How much did Medicare cost in 1970?
In 1970, some 7.5 billion U.S. dollars were spent on the Medicare program in the United States. Almost fifty years later, this figure stood at some 796.2 billion U.S. dollars. This statistic depicts total Medicare spending from 1970 to 2019.
What is Medicare coverage?
Increasing Medicare coverage. Medicare is the federal health insurance program in the U.S. for the elderly and those with disabilities. In the U.S., the share of the population with any type of health insurance has increased to over 90 percent in the past decade.
How much will Alzheimer's cost in 2020?
In 2020, Alzheimer's disease was estimated to cost Medicare and Medicaid around 206 billion U.S. dollars in care costs; by 2050, this number is projected to climb to 777 billion dollars.
What was the budget of 2010?
The 2010 budget was a return to Depression economics. The increase in spending was designed to restore the economy to a healthy 3.2% growth rate by 2011. Budget Deficit. The OMB original budget planned for a record $1.6 trillion deficit, but it actually came in at $1.294 trillion.
When was the 2010 budget passed?
The fiscal year 2010 was the Obama administration's first budget. It estimated revenue and spending from October 1, 2009, to September 30, 2010. It was passed on April 3, 2009, ahead of schedule.
What was the discretionary budget?
The Discretionary Budget was $1.37 trillion. This was due to a budgeted 13% increase in non-security spending to $695 billion. Spending for nearly all agencies was up across the board. The budget included $24 billion for jobs initiatives. This increase did not include the Economic Stimulus Bill funds, which had been moved to the Mandatory Budget.
What was the stimulus package for 2009?
The stimulus package increased spending on transportation, housing, and human services in FY 2009 and FY 2010. Many of these government programs had originally been created as part of the New Deal to provide a safety net for those who had been demolished by the Great Depression of 1929. The 2010 budget was a return to Depression economics. The increase in spending was designed to restore the economy to a healthy 3.2% growth rate by 2011.
How much did the government spend on TARP?
TARP. The government spent $151 billion on TARP in FY 2009. An additional $45 billion was budgeted in FY 2010 to bail out mostly community banks who were in danger of failing under too many subprime mortgages. But $110 billion was paid back by the large banks, actually adding revenue.
How does mandatory spending affect the economy?
How Mandatory Spending Affects the Economy. With over half the entire budget dedicated to mandatory programs, the Federal government was restricted in spending on programs to revive the economy, such as education, business loans, and even infrastructure.
How much was the FY 2012 budget?
In fact, mandatory spending was $1.954 billion. Here's the breakdown:
How many people are in Medicare Advantage in 2010?
In 2010, over 47 million are enrolled in one or both of Parts A and B of the Medicare program, and over 11 million of them have chosen to participate in a Medicare Advantage plan.
How is Medicare funded?
All financial operations for Medicare are handled through two trust funds, one for Hospital Insurance ( HI, Part A) and one for Supplementary Medical Insurance ( SMI, Parts B and D). These trust funds, which are special accounts in the U.S. Treasury, are credited with all receipts and charged with all expenditures for benefits and administrative costs. The trust funds cannot be used for any other purpose. Assets not needed for the payment of costs are invested in special Treasury securities. The following sections describe Medicare's financing provisions, beneficiary cost-sharing requirements, and the basis for determining Medicare reimbursements to health care providers.
How much does Medicare pay for prescriptions?
Beginning in 1991, Medicare pays 50 percent of the cost of outpatient prescription drugs above $600. When fully implemented in 1993, Medicare will pay 80 percent of prescription drug costs above a deductible that assumes that 16.8 percent of Part B enrollees will exceed the deductible.
What is the coinsurance for durable medical equipment?
Certain medical supplies and durable medical equipment may also be provided, although beneficiaries must pay a 20 percent coinsurance for durable medical equipment, as required under Part B of Medicare. There must be a plan of treatment and periodic review by a physician.
How many days are covered by Medicare?
The number of SNF days provided under Medicare is limited to 100 days per benefit period (described later), with a copayment required for days 21 through 100.
What is Medicare Advantage?
Medicare Advantage plans are offered by private companies and organizations and are required to provide at least those services covered by Parts A and B, except hospice services. These plans may (and in certain situations must) provide extra benefits (such as vision or hearing) or reduce cost sharing or premiums.
When did Medicare start for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis?
The 24-month waiting period (otherwise required for an individual to establish Medicare eligibility on the basis of a disability) is waived for persons with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, effective July 1, 2001. The entitlement to Medicare begins with the first month of the Social Security Administration's determination of eligibility for Disability Insurance benefits.
When did Obama start Medicare?
Medicare policy under the Obama Administration (2009-2017) Former President Barack Obama signed the Affordable Care Act (ACA) into law on March 23, 2010—establishing what would become one of the longest lasting legacies of his two terms in office. The ACA was enacted to achieve three main goals:
How long has Medicare been in effect?
Over 50 years have passed, and Medicare and Medicaid have since delivered on that promise and more—expanding coverage for prescription drug costs, long-term care patients, pregnant women, uninsured children, and disabled persons of all ages.
How much is Medicare reimbursement?
Medicare is a government-funded program. Because of this, provider reimbursement rates for the roughly 64 million Medicare enrollees are currently negotiated at about 90 percent of the full cost of a given treatment or procedure.
What is Medicare for all?
Medicare for all will create a two-tier market in which wealthy individuals pay for supplemental healthcare coverage outside of the universal insurance system, while others are funneled into an underfunded public healthcare model.
What is the lower drug cost now act?
Cummings Lower Drug Costs Now Act —legislation that now gives CMS the power to negotiate directly with pharmaceutical companies for lower Medicare drug costs, and to extend those same prices to Americans on private insurance.
When did Medicare reform start?
Medicare Reform: 2010 Through 2020 and Beyond. In 1965, former President Lyndon B. Johnson signed the Medicare and Medicaid bills into law with one mission in mind: to institute a national health insurance plan for older Americans and low-income families. Over 50 years have passed, and Medicare and Medicaid have since delivered on ...
What is the purpose of the ACA?
The ACA was enacted to achieve three main goals: Expand health insurance coverage in the United States . Control rising healthcare costs, and. Improve the quality of healthcare delivery. When the ACA was established in 2010, the United States had an uninsured population of nearly 50 million individuals.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/LifetimeLimitsBarryDownardIkonImages-5a884c21a9d4f9003613664c.jpg)
Summary
- Medicare, the federal health insurance program for nearly 60 million people ages 65 and over and younger people with permanent disabilities, helps to pay for hospital and physician visits, prescription drugs, and other acute and post-acute care services. This issue brief includes the most recent historical and projected Medicare spending data published in the 2018 annual repor…
Health
- In 2017, Medicare spending accounted for 15 percent of the federal budget (Figure 1). Medicare plays a major role in the health care system, accounting for 20 percent of total national health spending in 2016, 29 percent of spending on retail sales of prescription drugs, 25 percent of spending on hospital care, and 23 percent of spending on physician services.
Cost
- In 2017, Medicare benefit payments totaled $702 billion, up from $425 billion in 2007 (Figure 2). While benefit payments for each part of Medicare (A, B, and D) increased in dollar terms over these years, the share of total benefit payments represented by each part changed. Spending on Part A benefits (mainly hospital inpatient services) decreased ...
Causes
- Slower growth in Medicare spending in recent years can be attributed in part to policy changes adopted as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the Budget Control Act of 2011 (BCA). The ACA included reductions in Medicare payments to plans and providers, increased revenues, and introduced delivery system reforms that aimed to improve efficiency and quality of patient care …
Effects
- In addition, although Medicare enrollment has been growing around 3 percent annually with the aging of the baby boom generation, the influx of younger, healthier beneficiaries has contributed to lower per capita spending and a slower rate of growth in overall program spending. In general, Part A trust fund solvency is also affected by the level of growth in the economy, which affects …
Impact
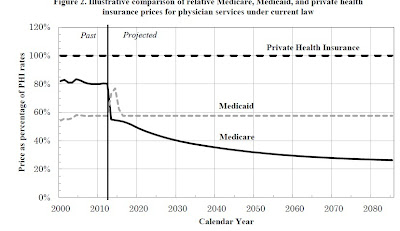
- Prior to 2010, per enrollee spending growth rates were comparable for Medicare and private health insurance. With the recent slowdown in the growth of Medicare spending and the recent expansion of private health insurance through the ACA, however, the difference in growth rates between Medicare and private health insurance spending per enrollee has widened.
Future
- While Medicare spending is expected to continue to grow more slowly in the future compared to long-term historical trends, Medicares actuaries project that future spending growth will increase at a faster rate than in recent years, in part due to growing enrollment in Medicare related to the aging of the population, increased use of services and intensity of care, and rising health care pri…
Funding
- Medicare is funded primarily from general revenues (41 percent), payroll taxes (37 percent), and beneficiary premiums (14 percent) (Figure 7). Part B and Part D do not have financing challenges similar to Part A, because both are funded by beneficiary premiums and general revenues that are set annually to match expected outlays. Expected future increases in spending under Part B and …
Assessment
- Medicares financial condition can be assessed in different ways, including comparing various measures of Medicare spendingoverall or per capitato other spending measures, such as Medicare spending as a share of the federal budget or as a share of GDP, as discussed above, and estimating the solvency of the Medicare Hospital Insurance (Part A) trust fund.
Purpose
- The solvency of the Medicare Hospital Insurance trust fund, out of which Part A benefits are paid, is one way of measuring Medicares financial status, though because it only focuses on the status of Part A, it does not present a complete picture of total program spending. The solvency of Medicare in this context is measured by the level of assets in the Part A trust fund. In years whe…
Benefits
- A number of changes to Medicare have been proposed that could help to address the health care spending challenges posed by the aging of the population, including: restructuring Medicare benefits and cost sharing; further increasing Medicare premiums for beneficiaries with relatively high incomes; raising the Medicare eligibility age; and shifting Medicare from a defined benefit s…