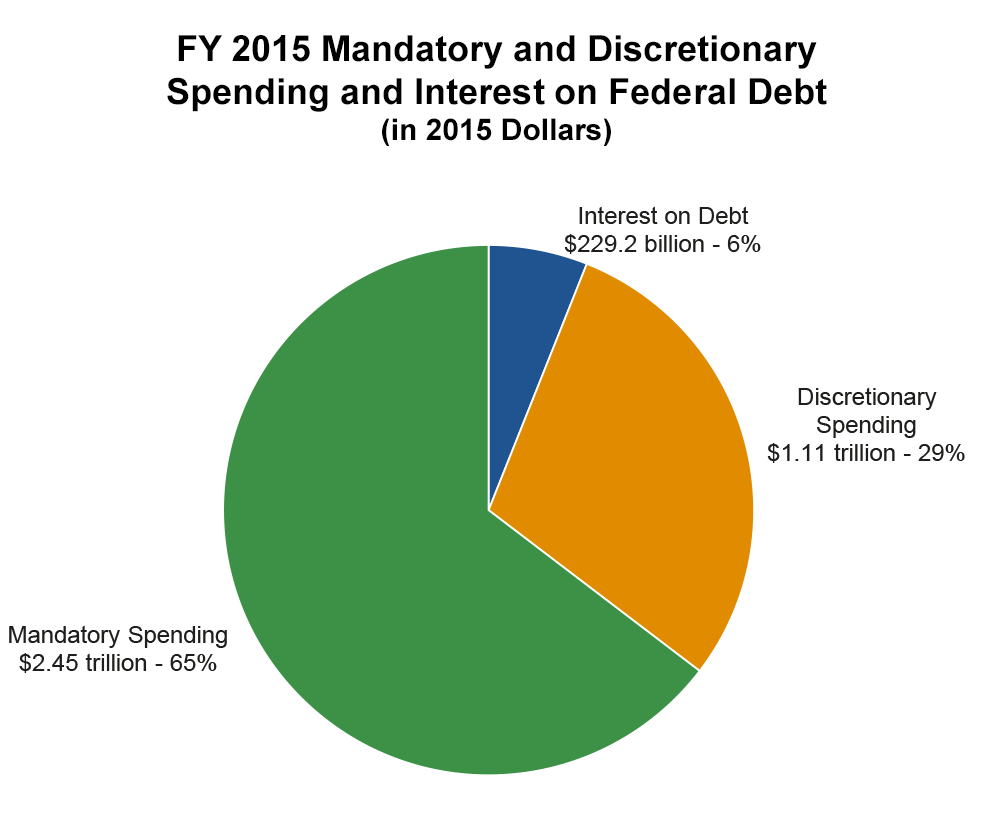
CMS Budget Overview
| Current Law | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2017 +/- 2016 |
| Medicare /1 | 546,228 | 595,317 | 609,541 | +14,224 |
| Medicaid /2 | 349,762 | 376,229 | 376,590 | +9,361 |
| CHIP | 9,242 | 14,470 | 15,015 | +545 |
| State Grants and Demonstrations | 589 | 633 | 543 | -90 |
How much of the federal budget is spent on Medicare?
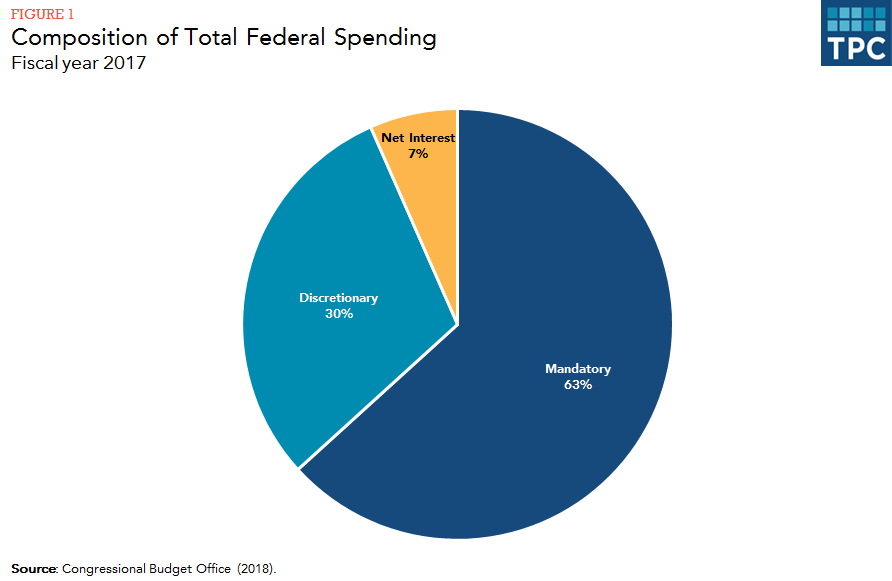
In 2018, Medicare spending (net of income from premiums and other offsetting receipts) totaled $605 billion, accounting for 15 percent of the federal budget (Figure 1). In 2018, Medicare benefit payments totaled $731 billion, up from $462 billion in 2008 (Figure 2) (these amounts do not net out premiums and other offsetting receipts).
What is the future of Medicare spending?
Medicare spending is a major driver of long-term federal spending and is projected to rise from 4 percent of gross domestic product (GDP) in fiscal year 2020 to about 6 percent in fiscal year 2051 due to the retirement of the baby-boom generation and the rapid growth of per capita healthcare costs. What Are the Components of Medicare?
What does the budget proposal for Medicare-Medicaid include?
The Budget includes four proposals to improve the quality and efficiency of care for Medicare-Medicaid, dually-eligible beneficiaries. See the Medicaid chapter for proposal descriptions. [$100 million in Medicare costs over 10 years] On April 16, 2015, the President signed the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015 (MACRA) into law.
How much will Medicare spending increase between 2018 and 2028?
Between 2018 and 2028, net Medicare spending is also projected to grow as a share of the federal budget—from 14.1 percent to 17.9 percent—and the nation’s economy—from 2.9 percent to 4.2 percent of gross domestic product (GDP).
How much is the CMS budget for 2017?
The FY 2017 Budget estimate for the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is $1.0 trillion in mandatory and discretionary outlays, a net increase of $26 billion above the FY 2016 level.
How much money did the Medicare budget save?
Most notably, the Budget saves $77.2 billion by reforming Medicare Advantage payments to improve efficiency and achieve sustainability of the program. Other proposals increase the value of Medicare payments to providers and address the rising costs of pharmaceuticals.
How does the Budget improve the long term sustainability of Medicare and Medicaid?
Other proposals in the Budget will improve the long-term sustainability of Medicare and Medicaid by increasing the efficiency of health care delivery without compromising the quality of care for the elderly, children, low-income families, and people with disabilities.
What is the budget proposal for private insurance?
The Budget proposes a series of private insurance proposals to promote transparency in health care and implement technical fixes to improve the administration of the Affordable Care Act. The Budget strengthens consumer protections, enhances CMS’ ability to verify Marketplace eligibility, and provides for a consistent definition of “Indian” to ensure all American Indian and Alaska Natives eligible for IHS services will be treated equally with respect to the Act’s coverage provisions, including access to qualified health plans without cost‑sharing requirements.
What is the budget for program management?
The Budget for Program Management enables reforms in health care delivery, while continuing to support the ongoing Medicare, Medicaid, and CHIP programs in CMS, as well as the Health Insurance Marketplaces. The request includes investments to address growing Medicare appeals workloads and improve the capacity and security of CMS’ information systems.
When did Obama announce the 2017 Medicare budget?
On February 9, 2016, President Obama unveiled his Fiscal Year 2017 Budget. [1] With respect to Medicare, this year’s proposed budget is very similar to last year’s, both good and bad, with some notable exceptions. While not a comprehensive analysis of all of the Medicare-related provisions, the Center for Medicare Advocacy provides these comments about the budget’s potential impact on Medicare beneficiaries, including their access to services and out-of-pocket expenses.
How much did Medicare spend in 2017?
The FY 2017 Budget includes a number of Medicare legislative proposals that would reduce net Medicare spending by $419.4 billion over 10 years. Unfortunately, approximately $56.4 billion of the total would be saved by implementing “structural reforms” that would shift additional costs directly onto Medicare beneficiaries. [9] The Center continues to oppose these proposals. We note that one provision that would have added a surcharge on Part B premiums for new beneficiaries who purchase Medigap policies with low cost-sharing, included in previous budgets, was excluded from the FY 2017 budget. Presumably, this is because Congress passed a physician payment bill in 2015 that imposes limitations on Medigaps purchased by new beneficiaries beginning in 2020. [10] Thus the concept is unfortunately already in the law.
What would the President's proposal do for Medicare?
Prescription drug rebates – The President's drug rebate proposal would restore the law to what it was before Part D , by allowing Medicare to benefit from the same rebates that Medicaid receives for brand name and generic drugs provided to beneficiaries who receive the Part D Low-Income Subsidy (LIS). Drug manufacturers would pay the difference between rebate levels already provided to Medicare Part D programs. Manufacturers would also be required to provide an additional rebate for brand name and generic drugs when their prices rise faster than inflation. Implementing drug rebates would save the Medicare program $121.3 billion over ten years.
How much is the CDC budget for 2017?
The FY 2017 Budget includes a total of $38 million, the same as FY 2016, to continue support for CDC’s implementation of laboratory safety recommendations.
How much did the FDA spend in 2017?
The FY 2017 Budget includes $1.5 billion for FDA to support implementation of the Food Safety Modernization Act, including increasing state capacity to implement the produce safety rules, implementing the Foreign Supplier Verification Program, and ensuring consumers are able to make healthy food choices.
How much did the Indian Health Service budget for 2017?
The Budget funds the Indian Health Service (IHS) at $6.6 billion, an increase of $402 million over FY 2016.
How much did the National Health Service Corps spend in 2017?
The Budget invests $380 million for the National Health Service Corps for FY 2017, which includes $70 million in additional mandatory and discretionary funding for behavioral health and supports the Administration’s opioid treatment and mental health initiatives.
How much money does the NIH spend on brain research?
Despite the many advances in neuroscience in recent years, the underlying causes of most neurological and psychiatric conditions remain largely unknown due to the vast complexity of the human brain. To further revolutionize our understanding of the brain, the Budget provides an $195 million within NIH, $45 million more than FY2016, for the Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies (BRAIN) Initiative. In collaboration with public and private partners, NIH is pushing the boundaries of neuroscience through the BRAIN Initiative to reveal how patterns of neural activity actually translate into emotion, thought, and memory. This research has the potential to discover underlying pathologies in a vast array of brain disorders and provide new avenues to treat, cure, and even prevent common conditions, such as Alzheimer’s disease, autism, depression, schizophrenia, and addiction. In FY 2017, the increased funds will continue to support basic neuroscience research, human neuroscience, neuroimaging, and training initiatives, as well as potential projects to collaborate with industry to test novel devices in the human brain, new ways to address big data from the brain, and develop devices for mapping and tuning brain circuitry.
How does the FDA work?
FDA ensures the safety, quality, and effectiveness of a broad scope of medical products. Within medical devices alone, FDA has oversight of at least 6,000 different product categories. FDA carries out these responsibilities while also leading the world in both numbers of new drugs approved and in the timeliness of their reviews. In 2015 alone, FDA approved 56 novel drugs and biological products. The Budget includes $2.8 billion, an increase of $116 million above FY 2016, to continue core medical product safety activities across FDA programs, including improving patient safety; developing the necessary infrastructure for a safer and more modern drug supply; and, continuing expanded and improved oversight of human drug compounding.
What is the HHS budget?
The Budget includes $51 million within the Office of the Secretary to increase the Department’s protections against cyber threats that pose risks to HHS critical functions, services, and data.
How much did the HHS budget save in 2017?
The President’s fiscal year (FY) 2017 Budget for HHS includes investments needed to support the health and well being of the nation and legislative proposals that taken together would save on net an estimated $242 billion over 10 years.
How much did the FDA spend in 2017?
The FY 2017 Budget includes $1.5 billion for FDA to support implementation of the Food Safety Modernization Act, including increasing state capacity to implement the produce safety rules, implementing the Foreign Supplier Verification Program, and ensuring consumers are able to make healthy food choices.
What is the HHS budget?
HHS has introduced proposals that will reward value and care coordination, rather than volume and care duplication. The Budget includes proposals to establish competitive bidding for Medicare Advantage payments and to introduce value-based purchasing for certain Medicare providers. These proposals are designed to increasingly align payments with costs and link payments to quality and value. The Budget also encourages participation in alternative payment models through a number of proposals, including creating a bonus payment for hospitals that cooperate with certain alternative payment models. The Budget also streamlines quality reporting and measurement by establishing a hospital wide readmissions reduction measure.
How does the Affordable Care Act work?
The Affordable Care Act is working to expand health insurance coverage to millions of Americans, including many gaining coverage and access to health care for the first time. The Budget builds on the successes of the Affordable Care Act by extending funding for the Children’s Health Insurance Program, improving and expanding coverage provided to American Indians and Alaska Natives through the Indian Health Service (IHS), expanding capacity in the nation’s health centers, making strategic investments in the health care workforce to increase access for rural and underserved populations, and targeting Medicare and Medicaid payments to better support primary and preventive care. The Budget continues to make investments in federal public health and safety net programs to help individuals without coverage get the medical services they need while strengthening local economies.
What is Medicare Part D?
The Budget also proposes to establish a program in Medicare Part D to prevent prescription drug abuse by requiring that high-risk beneficiaries only obtain controlled substances from specified providers and pharmacies.
Why is the budget important to HHS?
The Budget better positions the Department to fulfill its core mission to protect the health of Americans and provide essential human services. Investments in programs and the infrastructures that support them will improve transparency and efficiency across HHS. These improvements will allow HHS to not only meet the challenges of today, but also those of tomorrow.
How many people have access to the Affordable Care Act?
As a result, nearly 18 million Americans have gained coverage since enactment of the Affordable Care Act. As of January 2016, 30 states and the District of Columbia have elected to expand Medicaid to low income adults with household income up to 133 percent of the federal poverty level (Louisiana will make the 31st state). To encourage more states to take up this important option, the Budget would give any state that chooses to expand Medicaid eligibility three years of full federal support, no matter when the state expands. This common sense proposal makes expansion as good of a deal for states that choose to expand now as states that have already done so. Finally, the Budget includes an additional two years of funding for the Children’s Health Insurance Program through FY 2019 to align with the maintenance of effort requirement and ensure comprehensive and affordable coverage for beneficiaries as well as budgetary stability for states.
What is Medicare budget?
Budget Basics: Medicare. Medicare is an essential health insurance program serving millions of Americans and is a major part of the federal budget. The program was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson in 1965 to provide health insurance to people age 65 and older. Since then, the program has been expanded to serve the blind and disabled.
What percentage of Medicare is from the federal government?
The federal government’s general fund has been playing a larger role in Medicare financing. In 2019, 43 percent of Medicare’s income came from the general fund, up from 25 percent in 1970. Looking forward, such revenues are projected to continue funding a major share of the Medicare program.
What Are the Components of Medicare?
Medicare is a federal program that provides health insurance to people who are age 65 and older, blind, or disabled. Medicare consists of four "parts":
How Much Does Medicare Cost and What Does It Cover?
Medicare accounts for a significant portion of federal spending. In fiscal year 2020, the Medicare program cost $776 billion — about 12 percent of total federal government spending. Medicare was the second largest program in the federal budget last year, after Social Security.
How much of Medicare was financed by payroll taxes in 1970?
In 1970, payroll taxes financed 65 percent of Medicare spending.
How is Medicare self-financed?
One of the biggest misconceptions about Medicare is that it is self-financed by current beneficiaries through premiums and by future beneficiaries through payroll taxes. In fact, payroll taxes and premiums together only cover about half of the program’s cost.
How is Medicare funded?
Medicare is financed by two trust funds: the Hospital Insurance (HI) trust fund and the Supplementary Medical Insurance (SMI) trust fund. The HI trust fund finances Medicare Part A and collects its income primarily through a payroll tax on U.S. workers and employers. The SMI trust fund, which supports both Part B and Part D, ...
What percentage of Medicare is spending?
Key Facts. Medicare spending was 15 percent of total federal spending in 2018, and is projected to rise to 18 percent by 2029. Based on the latest projections in the 2019 Medicare Trustees report, the Medicare Hospital Insurance (Part A) trust fund is projected to be depleted in 2026, the same as the 2018 projection.
How much does Medicare cost?
In 2018, Medicare spending (net of income from premiums and other offsetting receipts) totaled $605 billion, accounting for 15 percent of the federal budget (Figure 1).
How is Medicare Financed?
Medicare is funded primarily from general revenues (43 percent), payroll taxes (36 percent), and beneficiary premiums (15 percent) (Figure 7) .
Why is Medicare spending so slow?
Slower growth in Medicare spending in recent years can be attributed in part to policy changes adopted as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the Budget Control Act of 2011 (BCA). The ACA included reductions in Medicare payments to plans and providers, increased revenues, and introduced delivery system reforms that aimed to improve efficiency and quality of patient care and reduce costs, including accountable care organizations (ACOs), medical homes, bundled payments, and value-based purchasing initiatives. The BCA lowered Medicare spending through sequestration that reduced payments to providers and plans by 2 percent beginning in 2013.
What is the average annual growth rate for Medicare?
Average annual growth in total Medicare spending is projected to be higher between 2018 and 2028 than between 2010 and 2018 (7.9 percent versus 4.4 percent) (Figure 4).
What has changed in Medicare spending in the past 10 years?
Another notable change in Medicare spending in the past 10 years is the increase in payments to Medicare Advantage plans , which are private health plans that cover all Part A and Part B benefits, and typically also Part D benefits.
How much did Medicare increase in 2018?
As a share of total Medicare benefit spending, payments to Medicare Advantage plans for Part A and Part B benefits increased by nearly 50 percent between 2008 and 2018, from 21 percent ($99 billion) to 32 percent ($232 billion) of total spending, as enrollment in Medicare Advantage plans increased over these years.
